How to Run Microsoft SQL Server|MSSQL in Docker on Windows
Posted January 16, 2024

If you want to run Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL) in Docker on Windows, this guide is for you. You will learn how to set up Docker Desktop for Windows and use it to run Microsoft SQL Server as a Docker container.
Running SQL Server (MSSQL) on Docker Desktop for Windows is an easy way to set up and manage SQL Server instances without the need for a dedicated server. This way, you run MSSQL without installing it but as a Docker container on your Windows machine. You will:
- Install Docker for Desktop.
- Create a Docker Container to run an SQL server on your Windows computer.
- Access Dockerized MSSQL Server using SQL Server client, i.e. SQL Server Management Studio.
Step 1: How to Set Up Docker Desktop for Windows
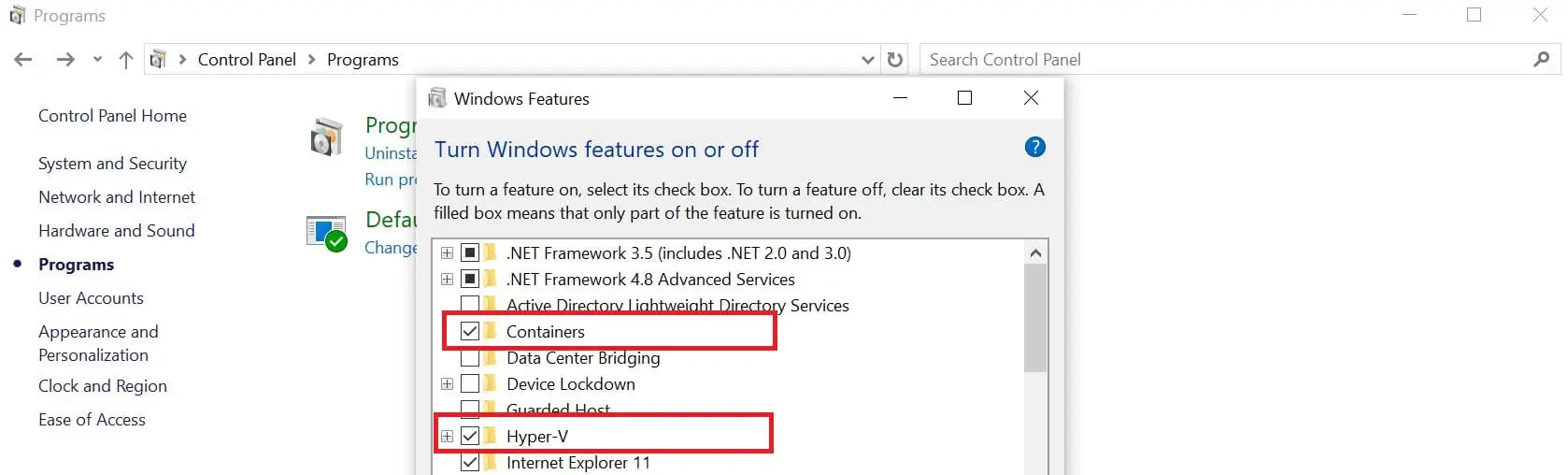
You first need to download Docker Desktop. Use that installer to install Docker. Before starting Docker, Enable the Hyper-V and Containers feature on your computer. You need to:
- Go to Control Panel on your Windows machine.
- Open Programs ⮕ Programs and Features ⮕ Turn Windows features on or off.
- Turn on Hyper-V and Containers Windows features and click OK to apply the changes.
Check this Comprehensive Guide on how to Install Docker Desktop on Windows
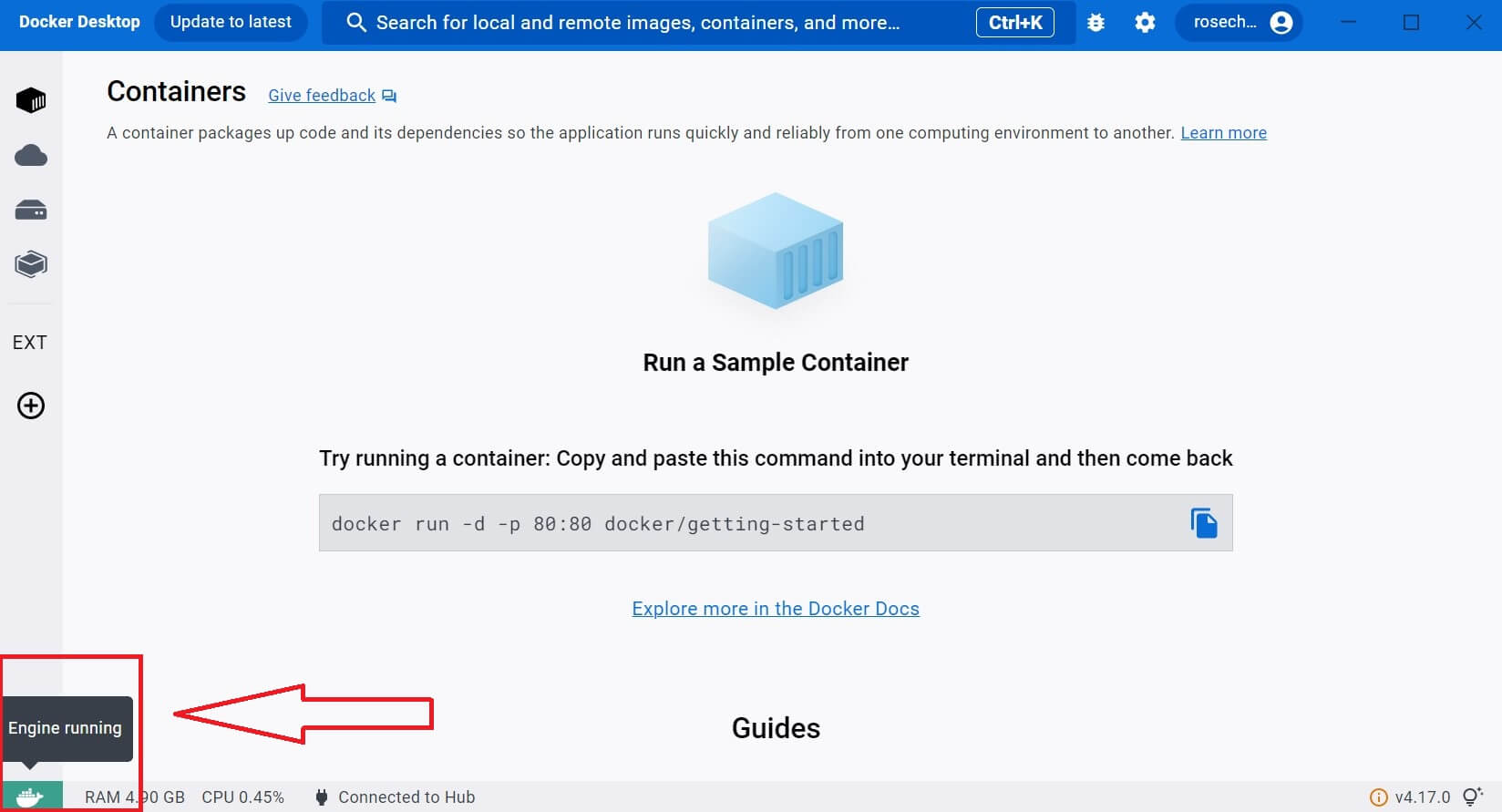
Once your computer restarts, Open the installed Docker Desktop Engine and make sure it is running as follows:
Step 2: How to Run MSSQL SQL Server Container with Docker on Windows
The installed Docker engine comes packaged with Docker Compose. Docker Compose uses a YAML file to define the services, networks, and volumes required to run SQL Server on Windows.
Therefore, you will run MSSQL as a Docker container in a single file while using Docker Compose.
Navigate to your working directory and create a docker-compose.yml file to deploy MSSQL on your Windows machine as follows:
version: '3.9'
services:
# SQL Server service
sql_server:
# Docker Image for MSSQL
image: mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server
environment:
- ACCEPT_EULA=Y
- SA_PASSWORD=Your@Password
ports:
- "1433:1433"
volumes:
- sql_data:/var/opt/mssql
# Named volumes section
volumes:
# SQL Server data volume
sql_data:
# Define the volume to persist SQL Server data
Now, in this code:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/serveris the Docker image to use for the SQL Server container on Windows. It will be pulled from Microsoft’s container registry.ACCEPT_EULA=Yaccepts the End-User Licensing Agreement for MSSQL.SA_PASSWORD=Your@Passwordwill automatically create a SA user and set the SQL Server user asYour@Password.- You need ports
"1433:1433"to expose the SQL Server between Windows bare metals and Docker Engine. - Note that port
"1433:1433"must be available. If not, change it to something like"1438:1433". - Volume
sql_data:/var/opt/mssql/datapersist SQL Server data. This way, database files survive container restarts, or if you turn off the Windows machine, the SQL Server data should persist and not be lost.
Step 3: Using Windows to Run SQL Server Docker Container
Now that you have the docker-compose.yml file ready, you need one command to have your SQL server ready.
Make sure you are in the file path and run the following command:
docker-compose up -d --build
This will Download and create a Docker service for MSSQL right on Windows as follows:
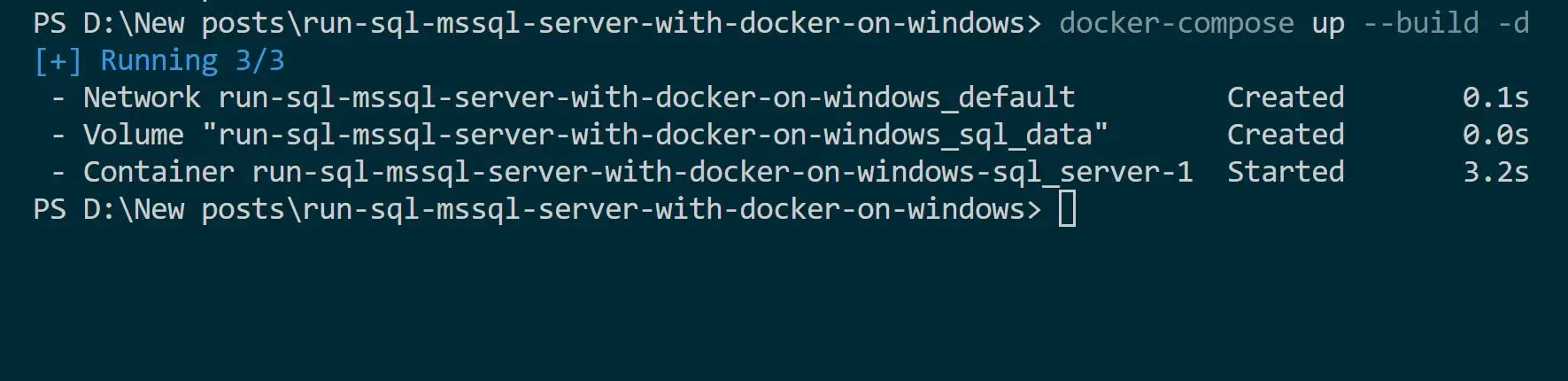
To confirm MSSQL is working, go to Docker Desktop and check its state as follows:
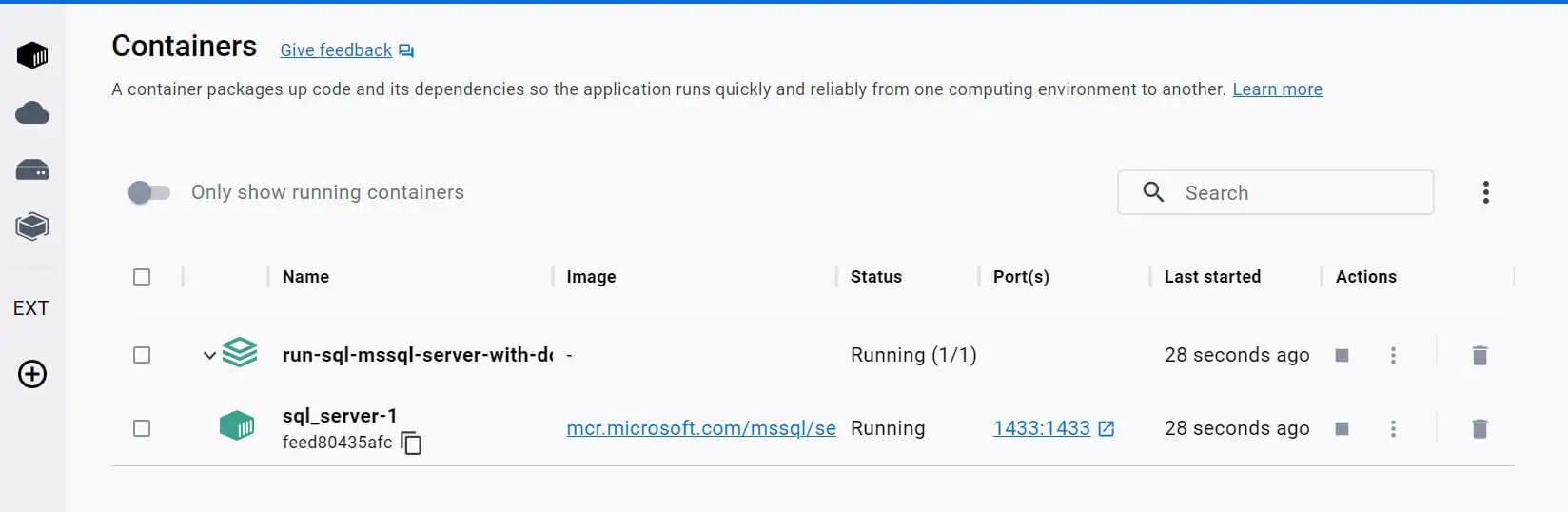
Step 4: Access MSSQL with SQL Server Management Studio
You need SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to manage an SQL Server. Once the container runs, SSMS will connect to the SQL Server instance within the container.
At this point, make sure you have downloaded and installed SSMS. Then Open it and use the following details to connect to MSSQL:
- Use
localhost,1433as the server name based on your Docker Compose port 1433. If you change it to 1438, update the server name as such. - Select SQL Server Authentication as the SQL Server Authentication strategy.
- The User name should be the default
sa. - The password in this case is
Your@Passwordbased on your Docker Compose File.
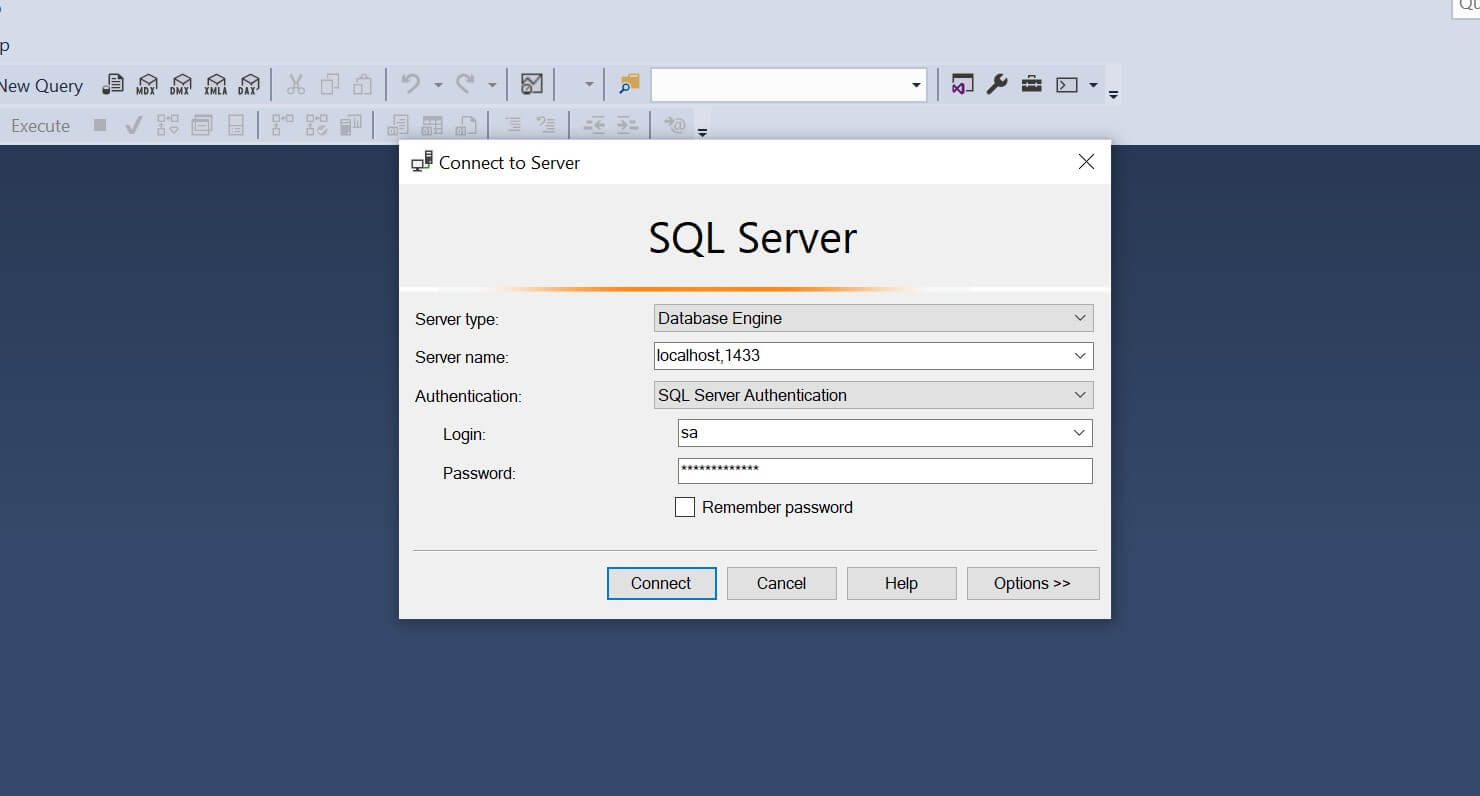
And SSMS Should be ready:
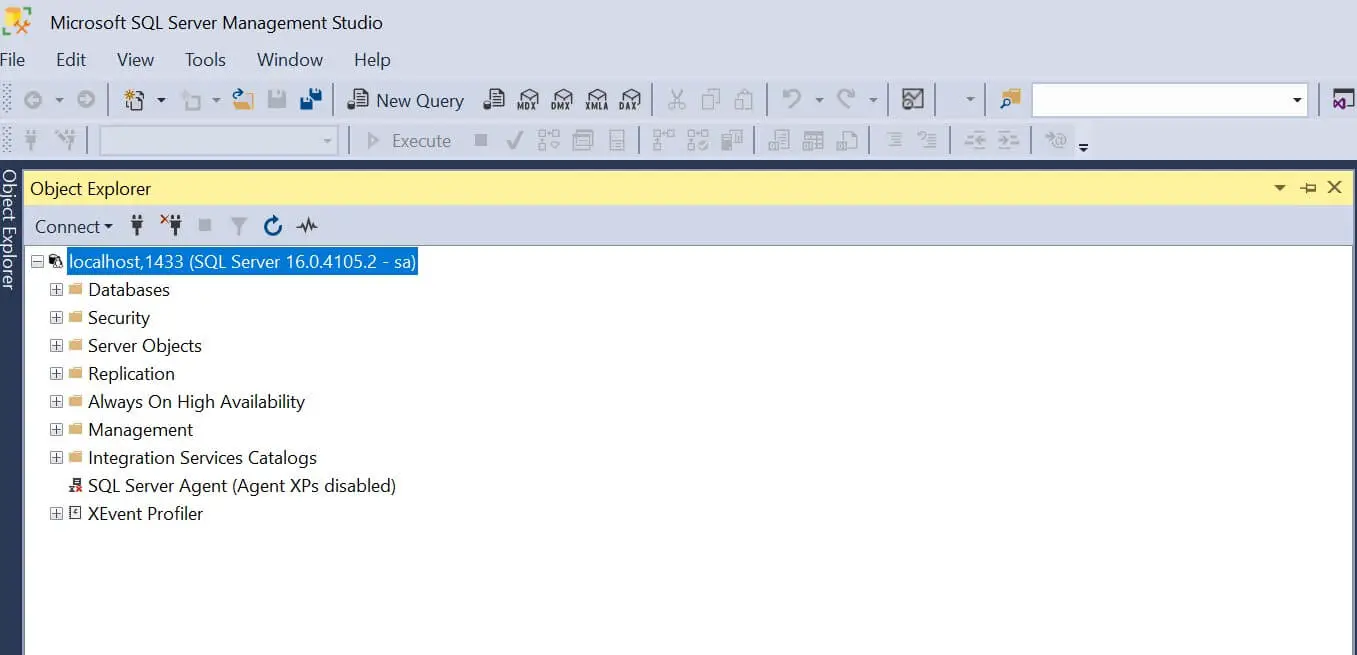
Step 5: Running Queries using Dockerize Windows SQL Server
To further confirm this SQL server is working, create a new database. Remember to add the user as sa:
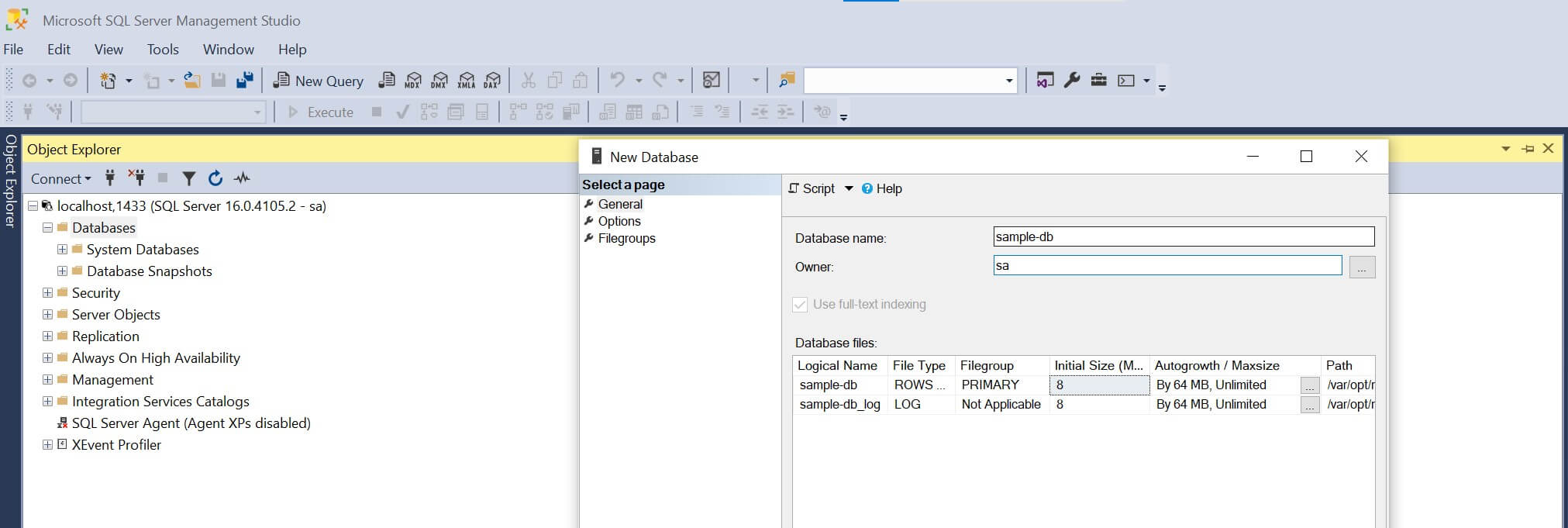
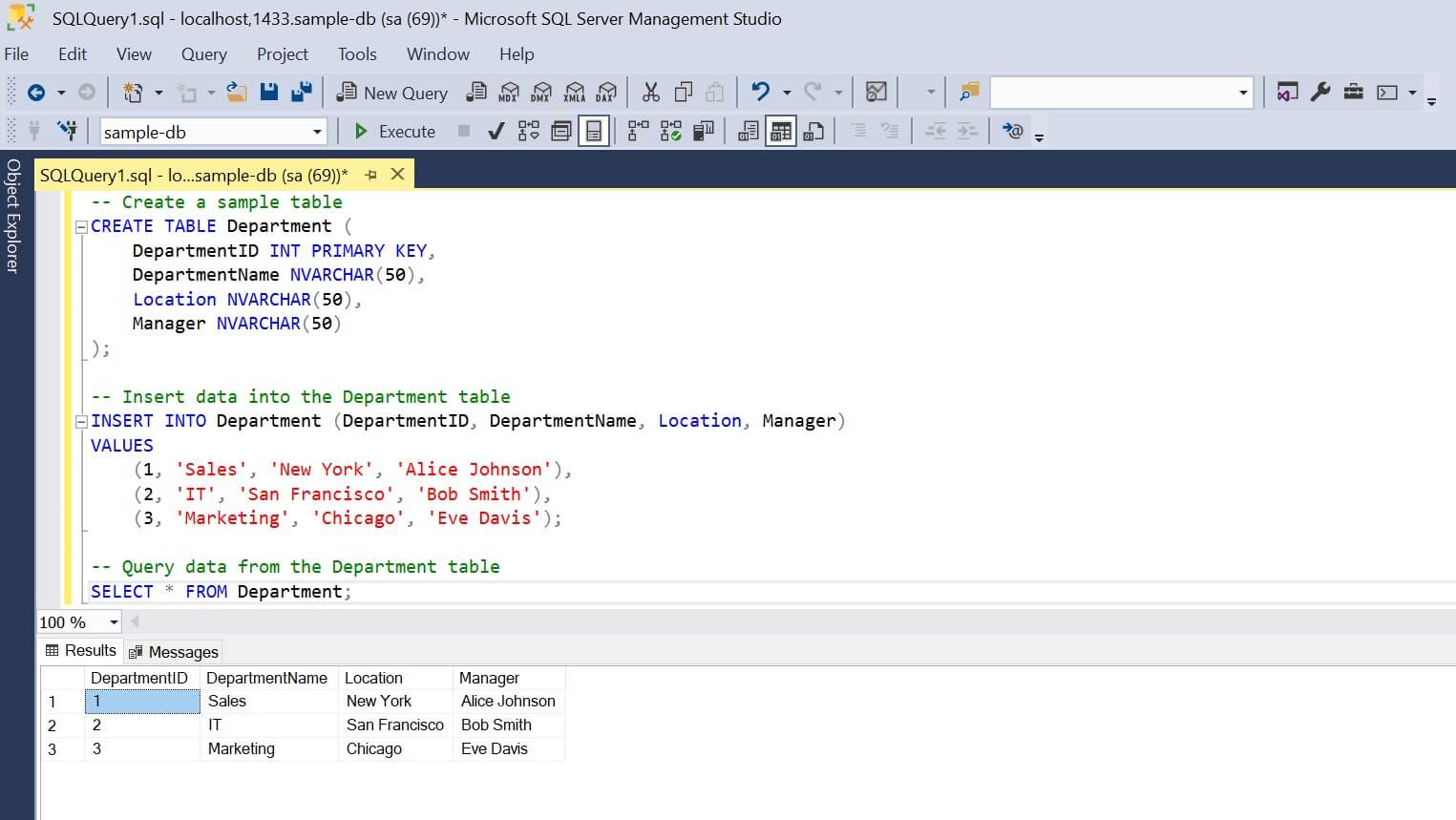
Let’s run the following SQL query to create a table and add some data while selecting the added records:
-- Create a sample table
CREATE TABLE Department (
DepartmentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
DepartmentName NVARCHAR(50),
Location NVARCHAR(50),
Manager NVARCHAR(50)
);
-- Insert data into the Department table
INSERT INTO Department (DepartmentID, DepartmentName, Location, Manager)
VALUES
(1, 'Sales', 'New York', 'Alice Johnson'),
(2, 'IT', 'San Francisco', 'Bob Smith'),
(3, 'Marketing', 'Chicago', 'Eve Davis');
-- Query data from the Department table
SELECT * FROM Department;
If SQL is correctly running within Docker Desktop for Windows, running this query should be successful as follows:
Conclusion
You have learned how to install Docker for Desktop and create a Docker Container to run an SQL server on your Windows computer. Now, go ahead and continue running your SQL queries.