How to use Xdebug docker php ext install and enable command
Posted October 30, 2023
Xdebug enhances debugging capabilities. Integrating Xdebug within Dockerized PHP environments further streamlines development workflows. However, to leverage Xdebug within Docker, commands such as docker php ext install xdebug and docker php ext enable xdebug install and enabled PHP to debug in the Docker environment.
This article meticulously teaches you the process of using docker php ext install xdebug, and docker php ext enable xdebug commands within Docker, and elevate your PHP Xdebug Docker environment.
Step 1: Setting up Dockerfile with PHP and Xdebug Extension
Dockerfile to run docker php ext install xdebug and docker php ext enable xdebug commands. In this scenario, consider the following PHP and Docker directory structure:
php-xdebug/
│ ├── xdebug.dockerfile
│ └── docker-compose.yml
└── xdebug/
└── index.php
Within the Dockerfile, use pecl install to install Xdebug and docker-php-ext-enable xdebug to enable it:
FROM php:7.4-apache
# Get the Xdebug extension
RUN pecl install xdebug \
# Enable the installed Xdebug
&& docker-php-ext-enable xdebug
# other configurations
pecl installis equivalent ifdocker-php-ext install xdebug. It will download and make Xdebug ready on Docker.- The
docker-php-ext-enablewill load the Xdebug PHP extension within a Docker container. This way, you make it available for use in PHP scripts and other attachable debugging environments.
Step 2: Creating PHP Container with Xdebug Extension and Docker Compose
Now use the docker-compose.yml file to create a PHP Xdebug container and expose your app to the web through Apache:
version: '3.9'
# Create an Apache PHP service (container)
services:
xdebug-app:
# Create a Docker Build context
build:
context: .
# Use the Xdebug Dockerfile as the container context
dockerfile: xdebug.dockerfile
# expose PHP to the web through Apache
ports:
- "9000:80"
# Copy ./xdebug APP folder to the container
volumes:
- ./xdebug:/var/www/html
environment:
# Configure Xdebug to connect to the host machine
XDEBUG_CONFIG: remote_host=host.docker.internal
# Add other environment configurations as needed
volumes copy your PHP code on xdebug to Docker. This way, your index.php file will be executed so your debugger can access it.
Step 3: Creating Xdebug Extension Verification Script
To test if Xdebug is working with Docker, I will create a small script that will return Xdebug when executed. This will tell you whether Xdebug is available on Docker or not.
Go to the xdebug/index.php file and add the following test code sample:
<?php
// Check if Xdebug is available on docker
if (function_exists('xdebug_info')) {
xdebug_info();
} else {
echo "Xdebug is not installed.";
}
?>
Step 4: Creating an Xdebug PHP Docker Container.
Run the docker-compose command to spin your PHP Container with the following command:
docker-compose up -d --build
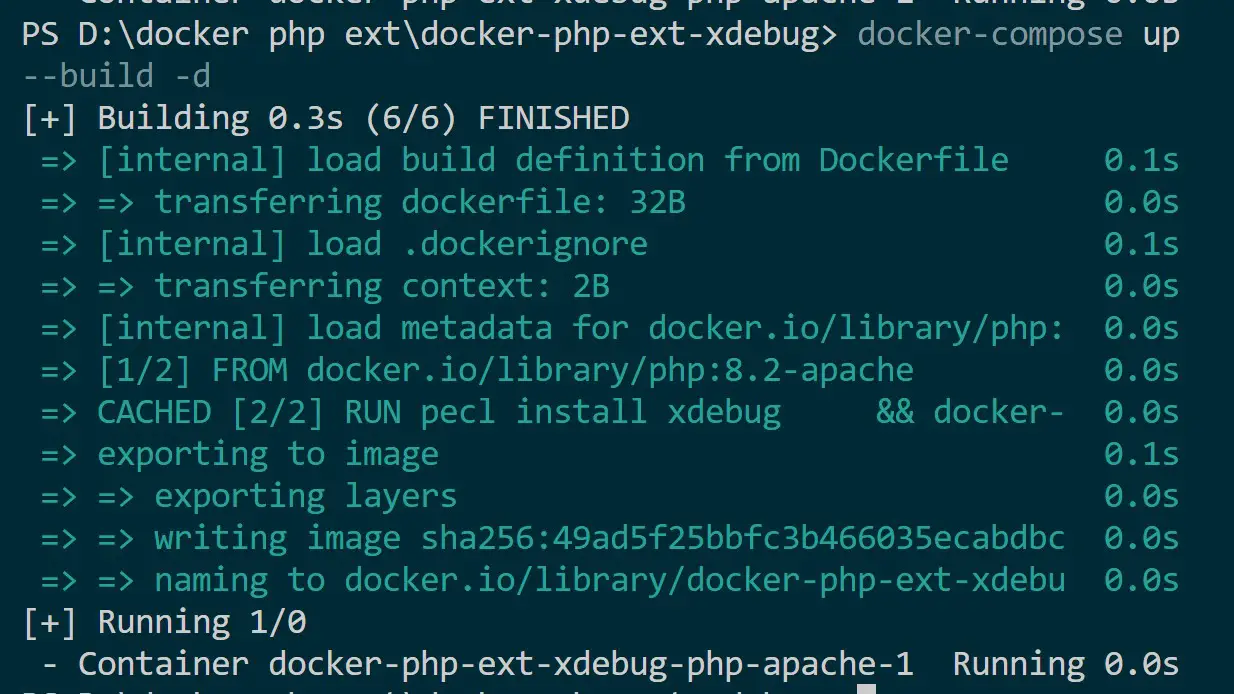
Go to Docker demons and Validate if your container is ready:
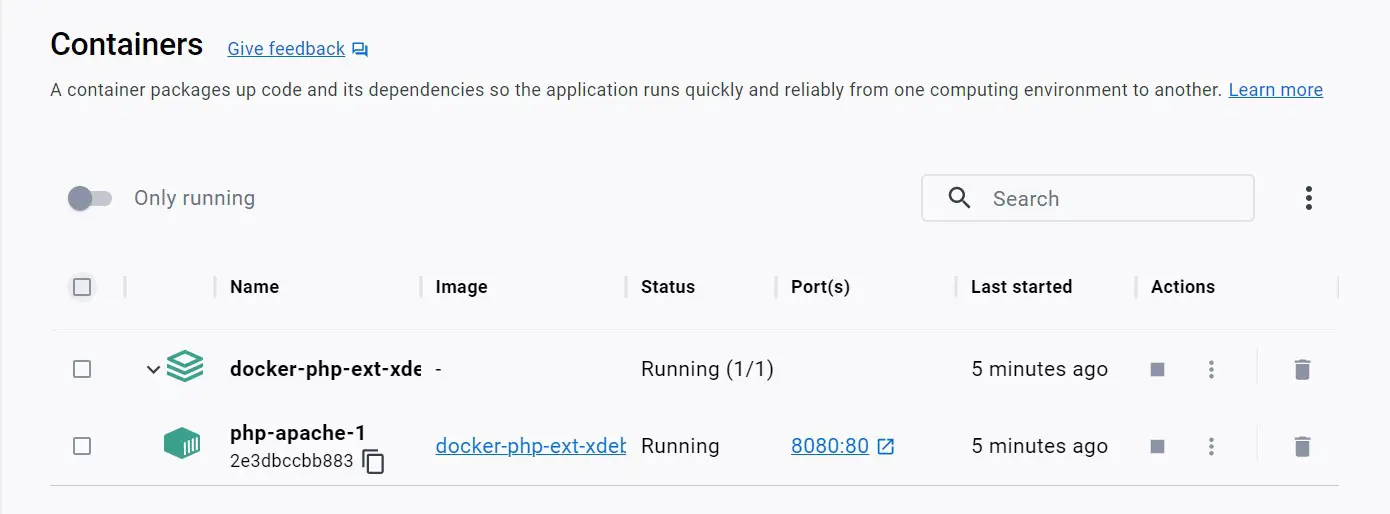
Open the appliction URL http://localhost:9000 in the browser. This should check and confirm if Xdebug is ready as such:
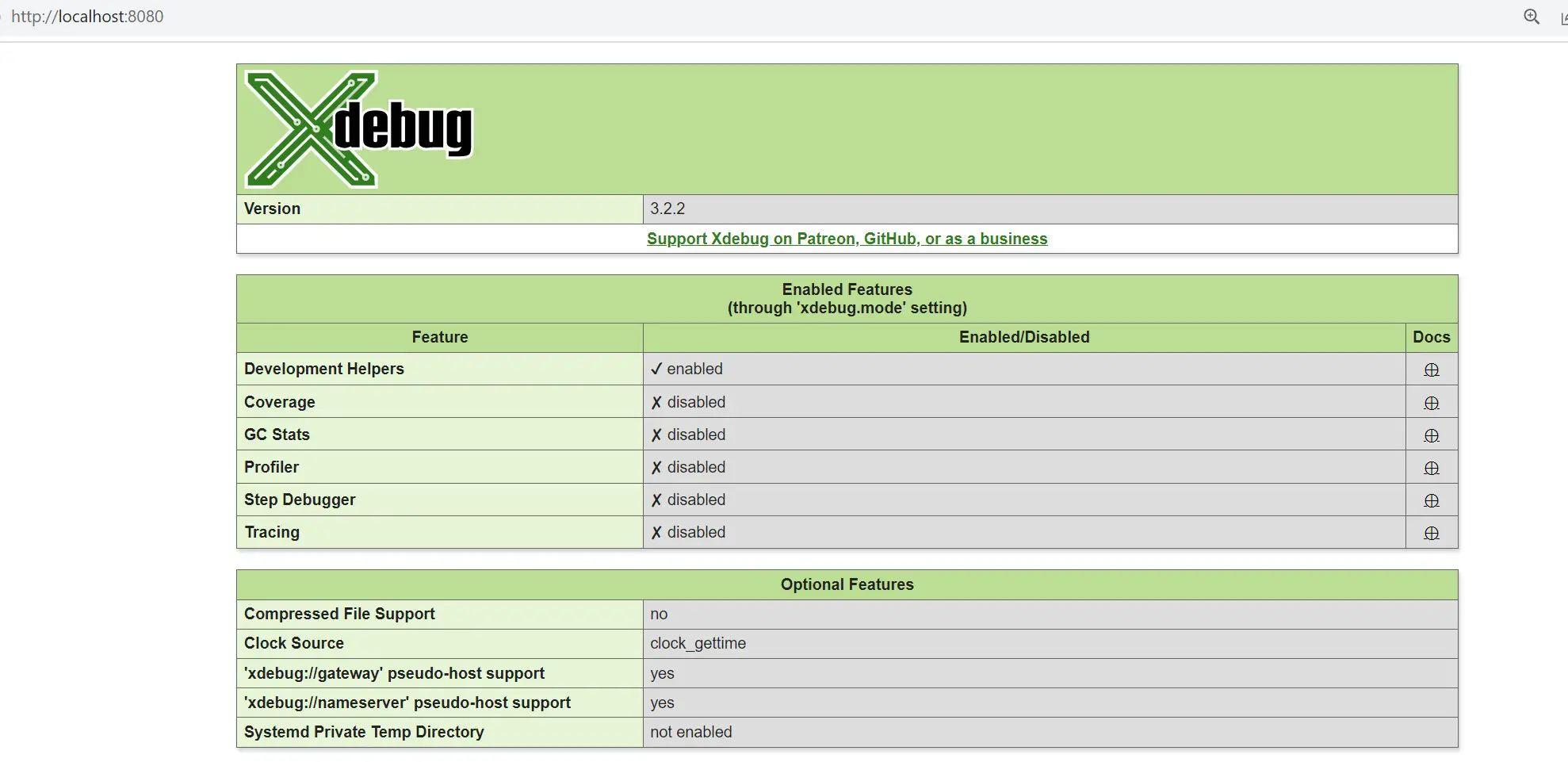
Conclusion
Xdebug integration within Docker using the php-ext-install command creates a great PHP development workflow. You have now installed, enabled, and configured Xdebug. You can now utilize Xdebug for debugging and profiling tasks within Docker to optimize your development experience.