Install and Deploy Portainer and Docker with Terraform
Posted March 4, 2024

Terraform manages your Docker containers and clusters through infrastructure-as-code principles. Portainer runs on Docker. This way, it’s very possible to use Terraform to deploy and run your Portainer Docker containers.
In this Guide, you will learn how to Install and Deploy Portainer and Docker with Terraform. I’ll outline the steps to set up Portainer using Terraform alongside code examples.
These are the Key Takeaways:
- How to add Terraform Docker provider
- Using Terraform to create Terraform-related Docker volumes.
- How Terraform pulls a Portainer image and spins a Docker Container.
Ready? Dive in and Install and Deploy Portainer and Docker with Terraform.
Related:
Step 1: Portainer Terraform Requirements
Before using Terraform to run Portainer, ensure:
- You have the basics of using Portainer.
- Have Terraform installed on your system.
Step 2: Setting up Terraform Portainer Configuration
First, create a directory for your Terraform configurations:
mkdir portainer-terraform
cd portainer-terraform
Use terraform init to initialize Terraform:
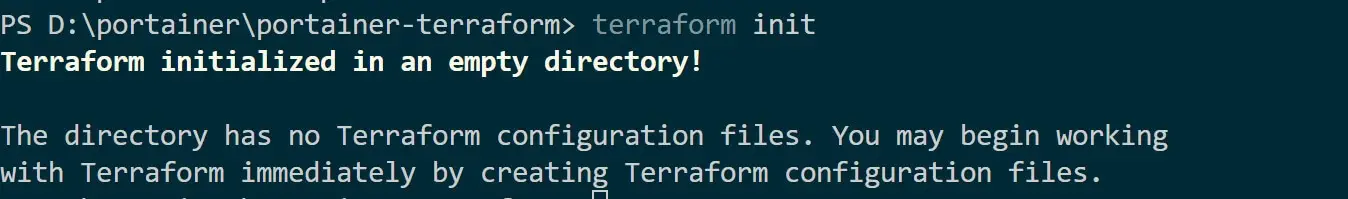
Create a main.tf file in your directory. Check the following steps to add Terraform Portainer configuration.
Step 3: Creating Terraform Docker Provider
Provider creates a communication between Terraform and your Docker Host. A Terraform provider will represent a named config for Docker communication.
In your main.tf file, create Docker provider as follows:
# Define the required provider and its version
terraform {
required_providers {
docker = {
source = "kreuzwerker/docker"
version = "3.0.2"
}
}
}
# Configure the Docker provider
provider "docker" {
# Specify the host for Docker communication
host = "npipe:////./pipe/docker_engine"
}
If you are using a UNIX system, your host should change as follows:
provider "docker" {
host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
}
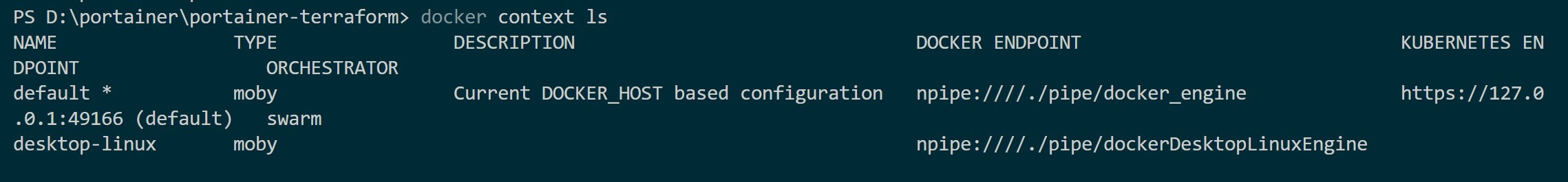
But to be on the safe side, always verify the docker current endpoint using the following command:
docker context ls
Should the copy and use the host, and it appears in your terminal:
Step 4: Creating Terraform Portainer Volume Resource
You want Portainer to persist its Data. To this with Terraform, you will create a Data resource in your main.tf file as such:
# Define a Docker volume resource for Portainer data
resource "docker_volume" "portainer_data" {
# Specify the name for the Docker volume
name = "portainer_data"
}
Step 5: Creating a Portainer Docker Container with Terraform
Terraform will use a Docker Container Resource to create a Portainer. In this case, you will have:
- Portainer Docker image.
- maps port 9000 from the container to the host.
- Add
volumesblock mounts theportainer_datavolume into the container. - Added to mount the Docker socket (
/var/run/docker.sock) into the container.
All this will allow Terraform to create a Portainer container to interact with the Docker daemon. Add them in the main.tf file as follows:
# Docker container resource for the Portainer service
resource "docker_container" "portainer" {
# Nname the Docker container
name = "portainer"
# Docker image to use for the container
image = "portainer/portainer-ce:latest"
# Port mapping for accessing Portainer
ports {
internal = 9000
external = 9000
}
# Restart the policy for the container
restart = "always"
# Volume mounts for the container
volumes {
# Mount the Docker volume created earlier into the container
volume_name = docker_volume.portainer_data.name
container_path = "/data" # Mount path within the container
}
# Mount the Docker socket into the container
volumes {
host_path = "/var/run/docker.sock" # Host path to Docker socket
container_path = "/var/run/docker.sock" # Container path to Docker socket
}
}
Step 6: Deploying Portainer Docker Container with Terraform
Terraform uses three commands:
- terraform init
- terraform plan
- terraform apply
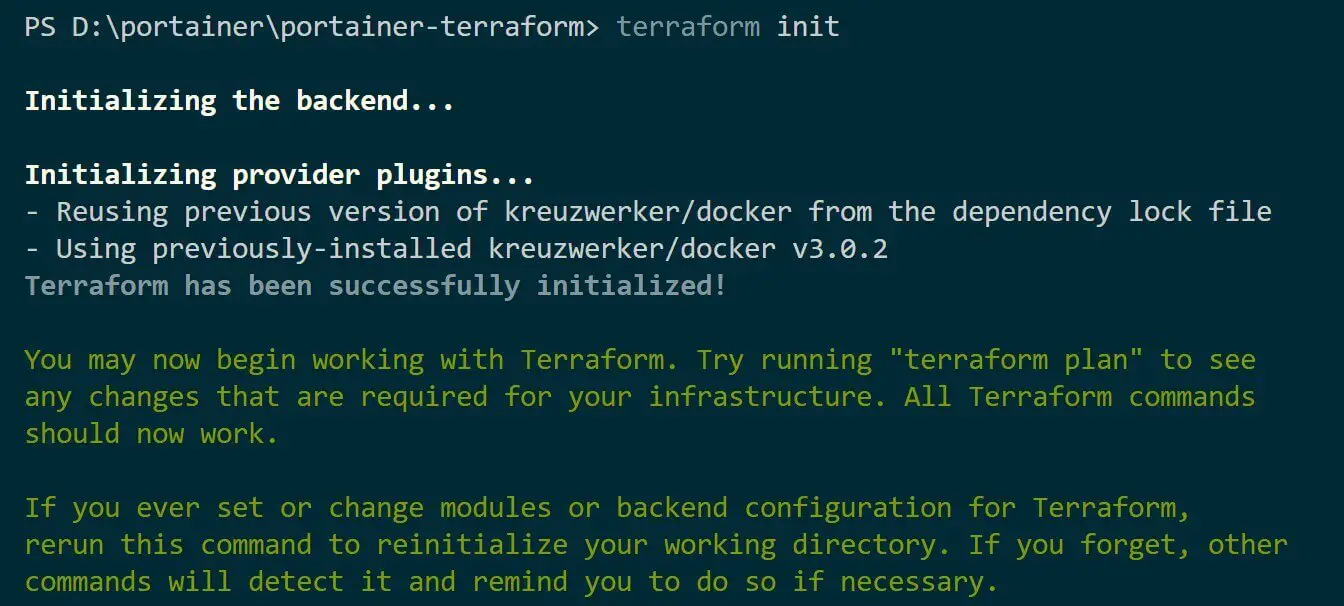
These commands will be enough to let Terraform run a Portainer. Start with terraform init to initialize Terraform in the directory containing your configuration files:
terraform init
It will initialize the current directory as a Terraform workspace and download Docker provider to run Portainer:
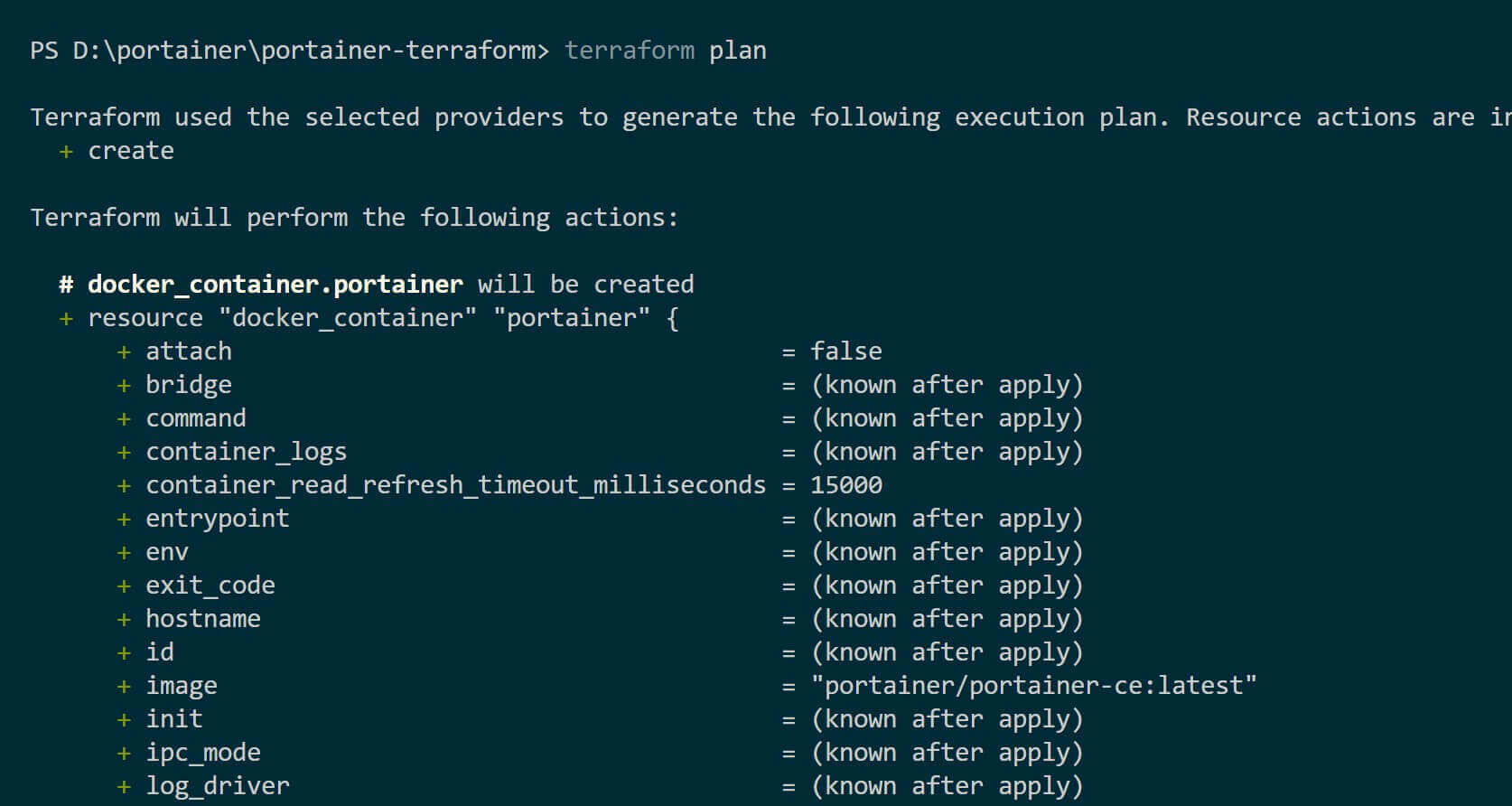
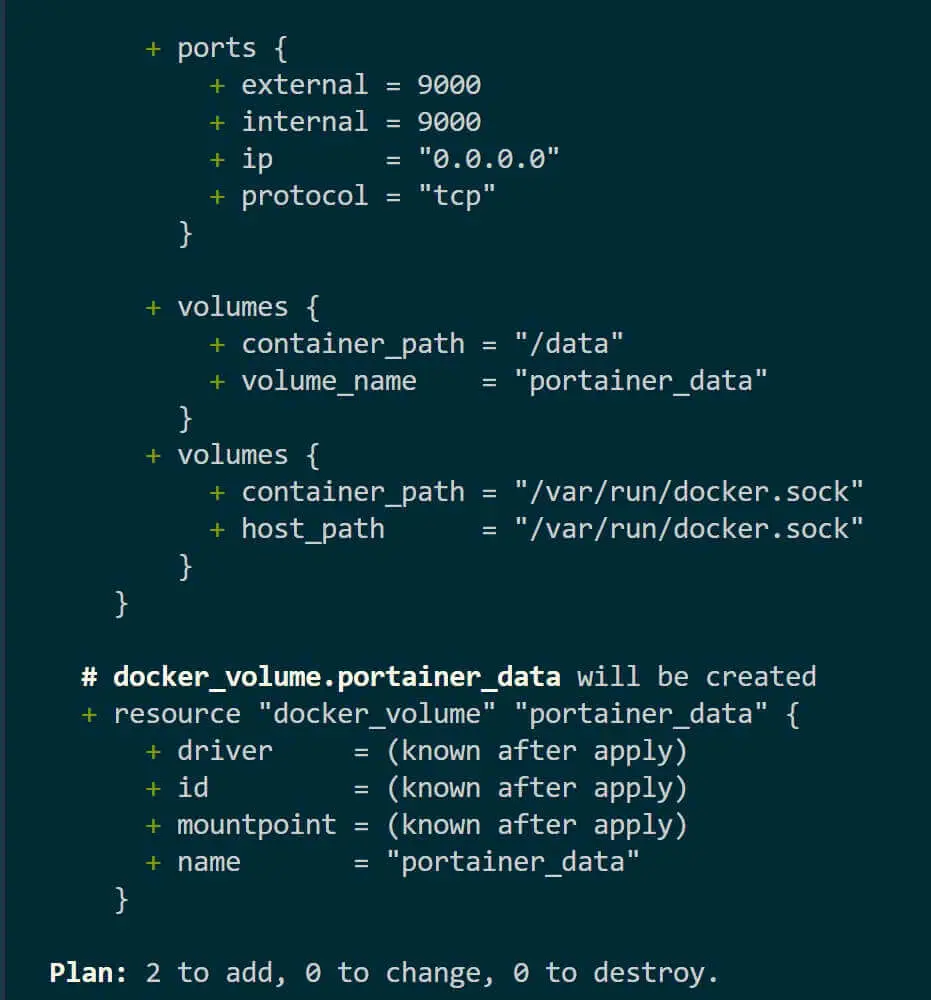
terraform plan create an execution plan to preview the changes that Terraform will make to your infrastructure:
terraform plan
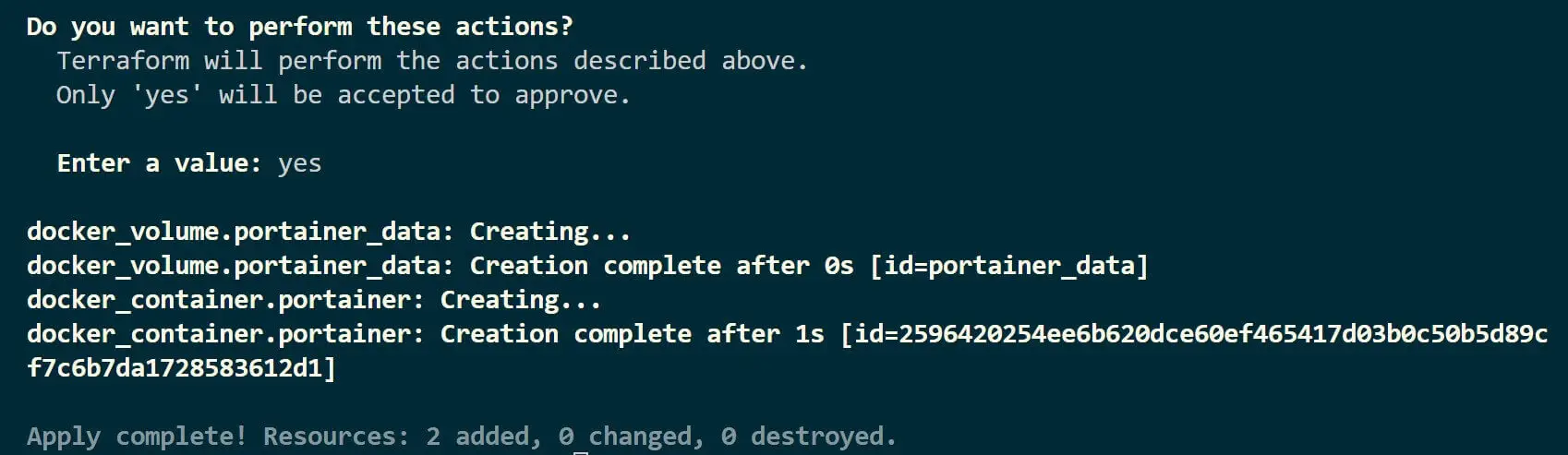
Finally, use the terraform apply command to apply the changes to your infrastructure:
terraform plan
Terraform will prompt you to confirm the execution plan. If everything looks correct, type yes and press Enter:
Step 7: Accessing the Deployed Terraform Portainer Server
First, use Docker to make sure you have a running Portainer container:
docker ps
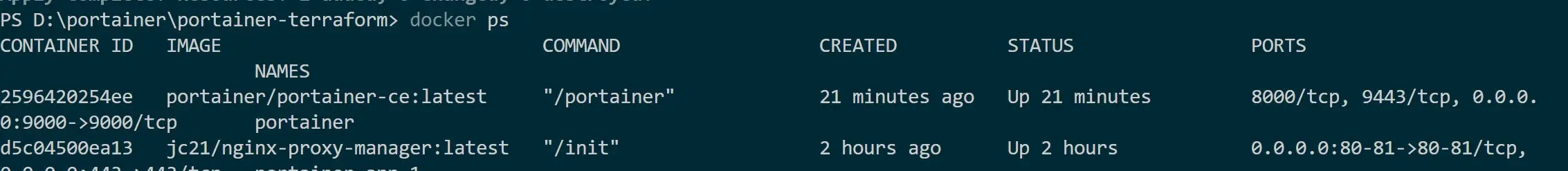
Docker should be running, and you should have the same if you are using Docker Engine UI:
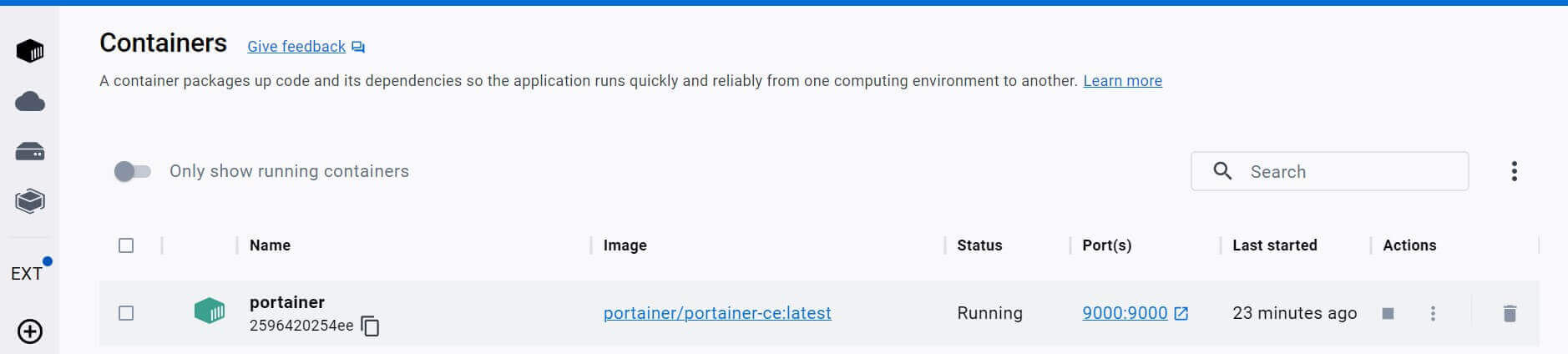
Terraform has successfully Deployed Portainer, and it’s running on port 9000. Access it using http://<DOCKER_HOST>:9000. or http://<your_server_ip>:9000.
If you get an error like this:

Restart the Portainer container with Docker:
docker restart portainer
Go ahead and:
- Create User:
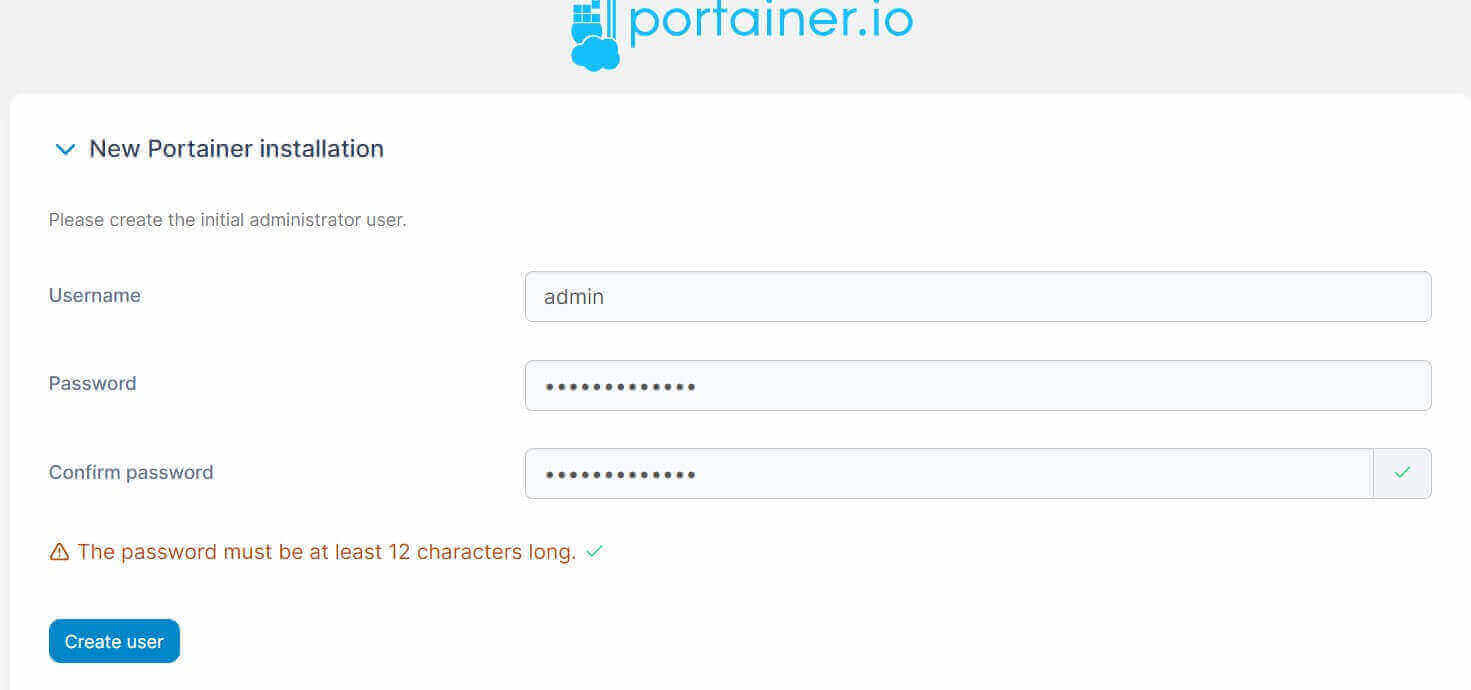
- Once you Log in and Get Started to add the local environment:
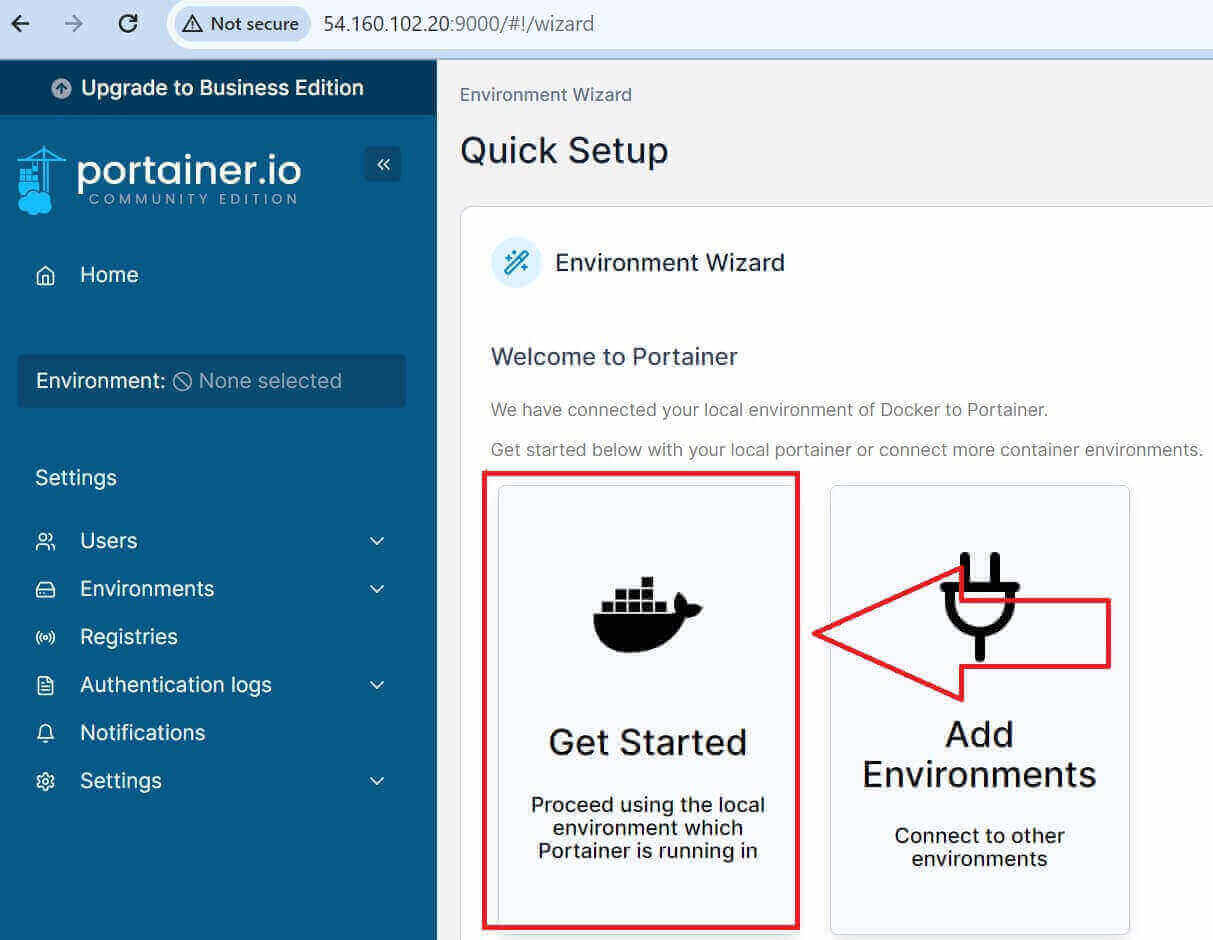
- Now you have the environment as follows:
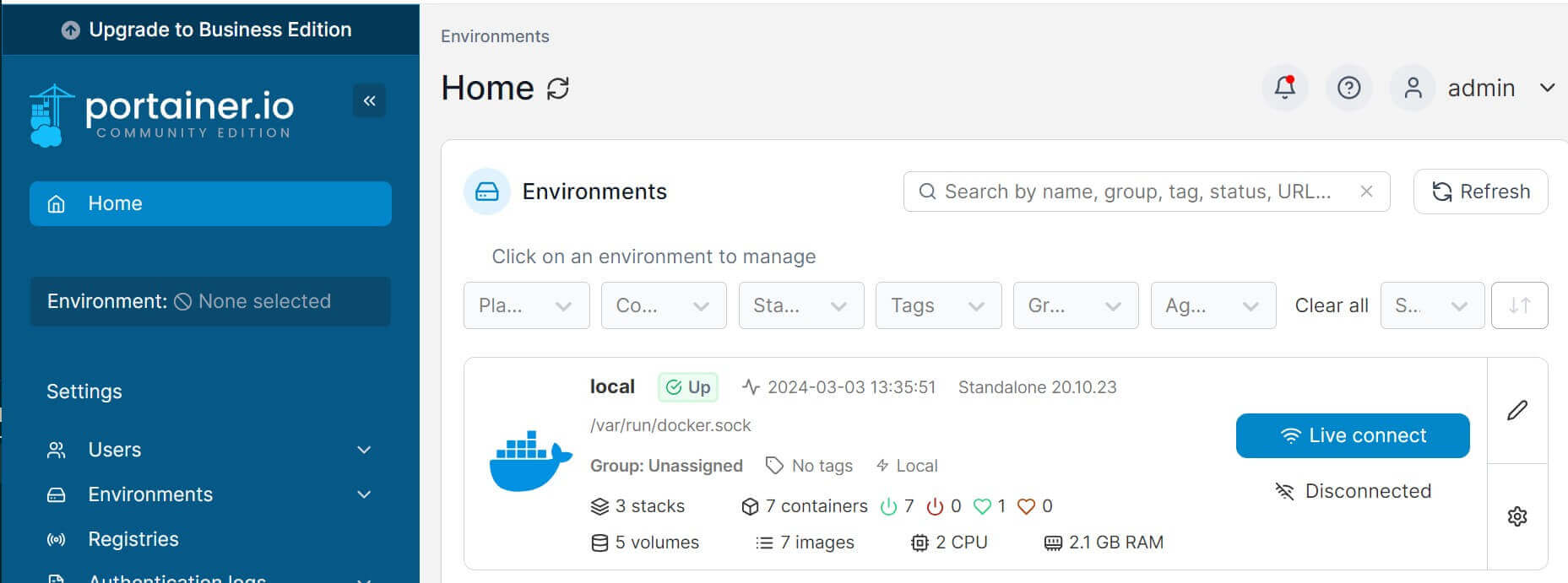
- Click the local environment and access your Portainer dashboard:
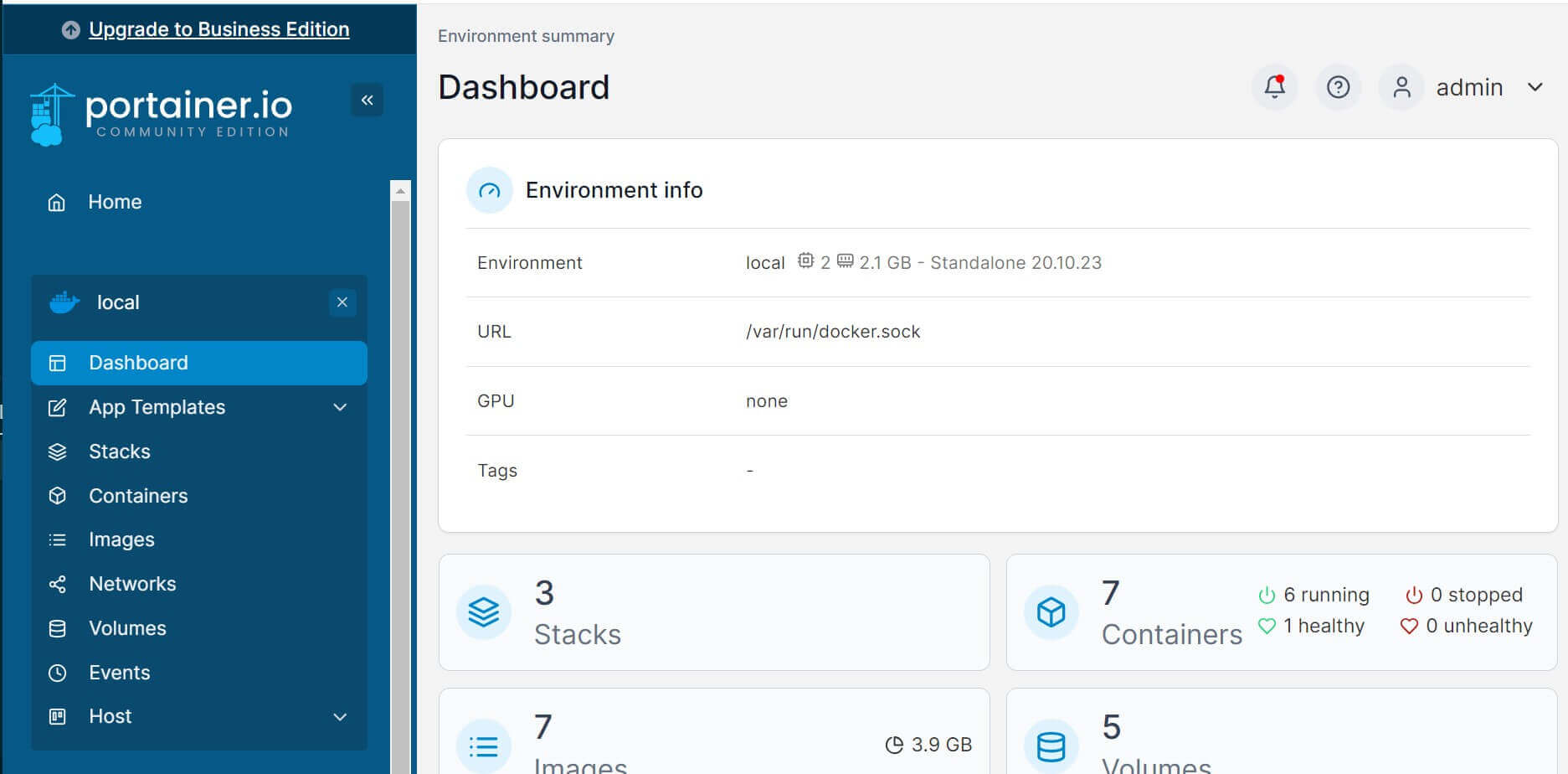
If you want to tear down the Portainer container created by Terraform, use the following command:
terraform destroy
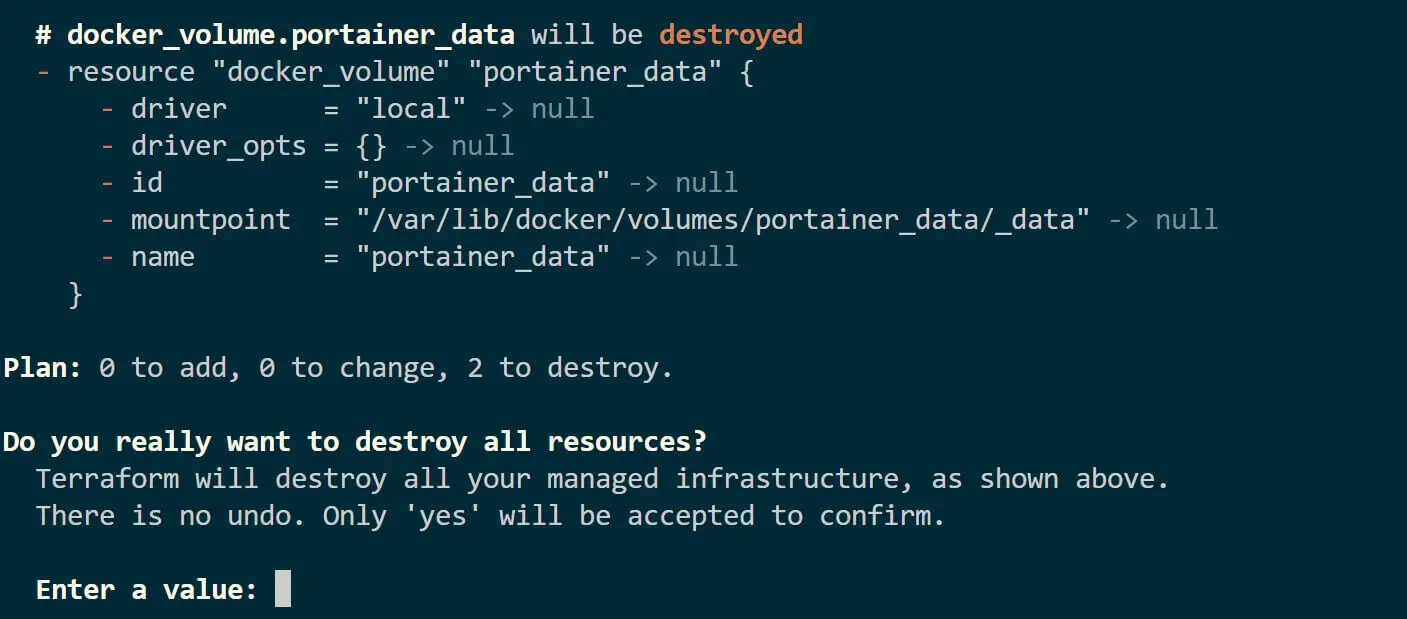
You have learned how to use Terraform to run Portainer. I hope you can now:
- Add Terraform Docker provider.
- Use Terraform to create Terraform-related Docker volumes.
- Use Terraform to pull a Portainer image and spin a Docker Container.



