Run|Pull Minikube Local Docker Image Registry on Kubernetes
Posted October 6, 2023

It’s always a challenge to let Kubernetes use a local docker image. In this post, you will deploy Kubernetes cluster locally using a Minikube local development docker registry to run Kubernetes local Kubernetes clusters via Minikube.
Dive into this guide, deploy and run Kubernetes locally using the Minikube registry and local Docker Images. Kubernetes will use Minikube to pull images from the local docker registry and create a cluster.
You will create three Minikube local registry methods to let Kubernetes pull local Docker images as such:
- Use Minikube as a Docker environment Variable.
- Pull local images using Minikube Docker Registry Build Command.
- Allow Minikube to Load Docker images to the local registry and not DockerHub.
Why Use a Local Minikube Docker Images Registry
You need a remote image to run a Kubernetes cluster. However, using Minikube local development, you can create and run Kubernetes locally via Minikube.
This way, you don’t have to use a DockerHub registry to spin up a local Kubernetes cluster. And that’s why Minikube comes into play.
What You Will Learn
Dive into this guide and learn the three ways to run Kubernetes locally using a Minikube development docker registry.
You will learn:
- How to pull and use Kubernetes local image registry/repository
- Create a Minikube docker registry locally
- Use Minikube local registry to spin a local Kubernetes cluster that pulls local Docker Images.
Prerequisites for Local Minikube Registry
To follow along, ensure you have:
- Docker Desktop installed and running on your computer
- Some basic Knowledge working with Kubernetes will be excellent.
Getting Local Minikube Registry up and Running
Once your Docker Desktop is ready, head over to Minikube docs and Install the Minikube docker registry. Then start your local Minikube cluster using the following command:
minikube start
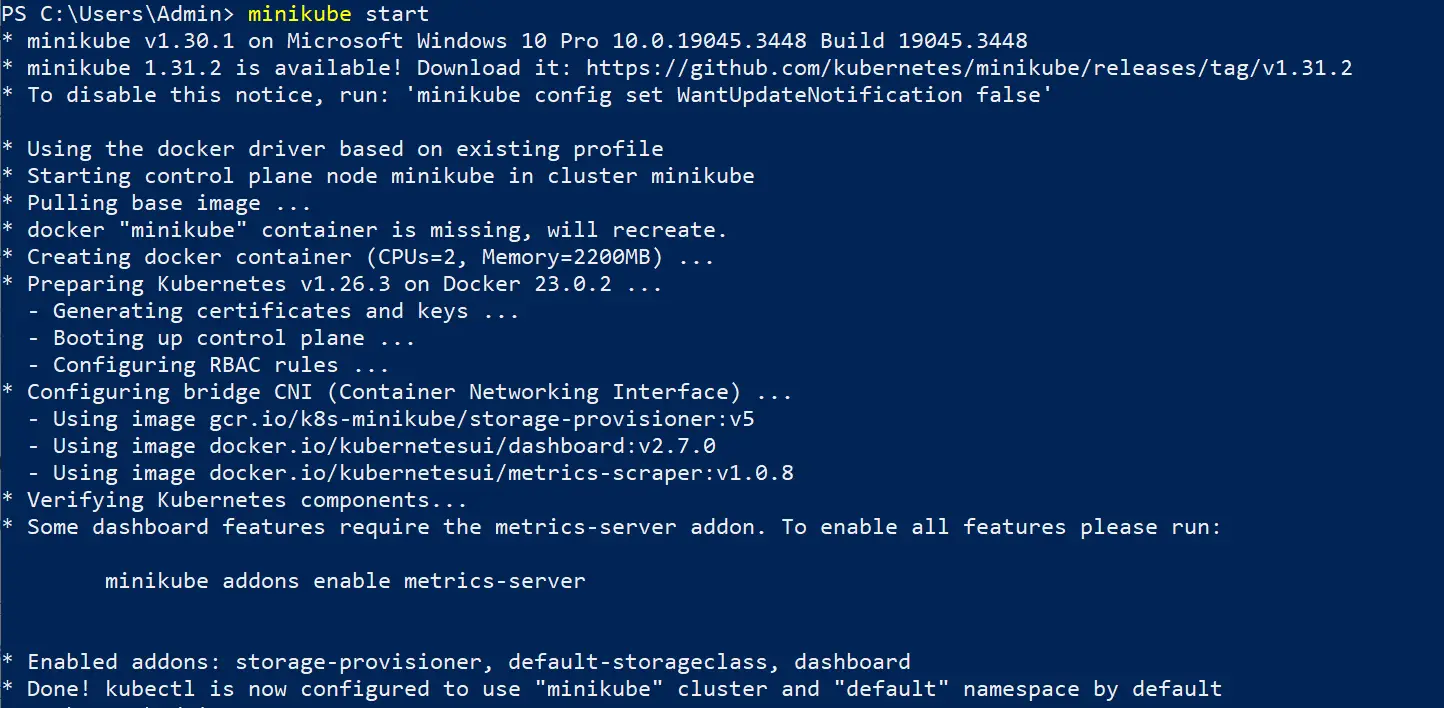
Now confirm your Minikube registry is running:
kubectl cluster-info
This should give you a sample result as follows, telling your Minikube Docker Registry is ready for development and running on localhost:

Creating a Sample App to Get Kubernetes Docker Image Up and Running
You need a sample app. If you don’t have one, use Node.js and create the following simple hello world API:
- Initialize your app using
npm init-yto get the API framework ready. - Create your app.js file with the following simple Nodejs hello world app:
// app.js
const http = require('http');
// server host
const hostname = 'localhost';
// The port
const port = 3000;
// HTTP server handling requests
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// HTTP response status
res.statusCode = 200;
// headers
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
// Your response body"
res.end('Hello, World!');
});
// Start the server
server.listen(port, hostname, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`);
});
- To run your Docker image, use the following code. However, make sure you have created
Dockerfilefile in your root directory
# Node.js runtime as the base image
FROM node:18-alpine
# container working directory
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
# Copy all source code to the container
COPY . .
# Expose the port
EXPOSE 3000
# start the application
CMD [ "node", "app.js" ]
You will use this Docker image and run it on Kubernetes. You won’t run in remotely.
So, let’s dive and use Minikube to run a Kubernetes local image repository directly from your machine.
How Your Local Kubernetes Manifest Should Be
Initially, you would use a remote. However, when using a local Minikube registry, your manifest will change some parameters. Ensure you have your deployment manifest ready. Create a deployment.yml file as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3 # Set the number of replicas (pods) you want to run
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
containers:
- name: node-app
image: your-image-name # Replace with your Docker image
imagePullPolicy: Never
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
# Add your Service here
Keynote to check here are:
- Ensure you have
imagePullPolicyset toNever. Your cluster won’t hit the internet, and you are just using your Locally built docker image, soimagePullPolicycan’t be set asAlways. imageshould takeyour-image-name. But this time, your image name is local. So, it should be the name you use to build your image. For example, in thedocker build -t nodejs-app .command,nodejs-appwill be your image name for yourdeployment.ymlmanifest.
Building Image Locally with Minikube Docker Registry.
Now, let’s get to your Minikube local registry. Here, I will provide you with three solutions to running Kubernetes locally using a Minikube development docker registry:
SOL 1: The Hardest Way: Use Minikube Env Variable
Docker saves images locally to your host machine. However, you can let Minikube save the image and make it available locally. Go ahead and use the following command:
NOTE: This will only be using PowerShell if you are using Windows.
# LINUX centOS, Ubuntu
eval $(minikube docker-env)
# Only Windows PowerShell
minikube docker-env | Invoke-Expression
💡 Very Important: Your
envcommand must be executed in the same shell/current shell session you will use to run yourdocker buildcommand.
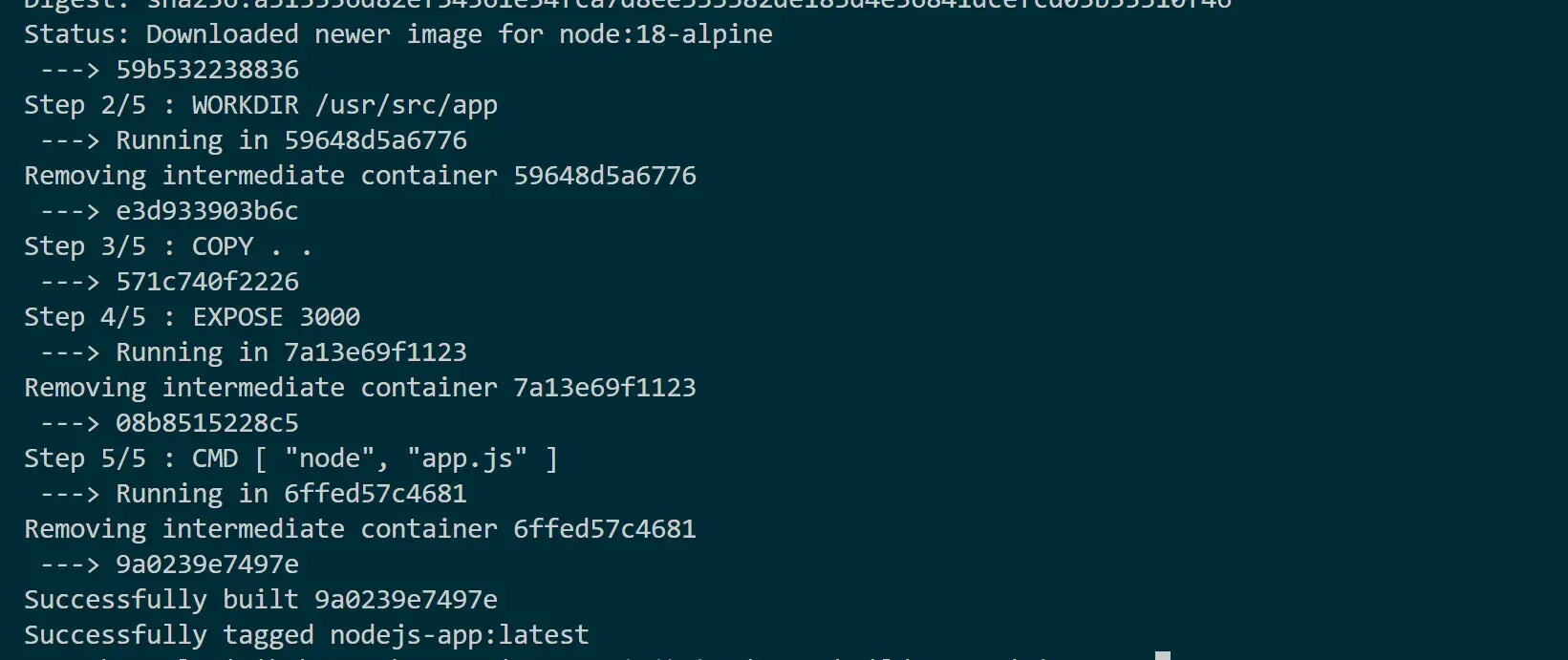
Once you have executed your command, rebuild your Docker image:
docker build -t nodejs-app .
This way, you can now check any Minikube local development docker image using the following command:
minikube image ls
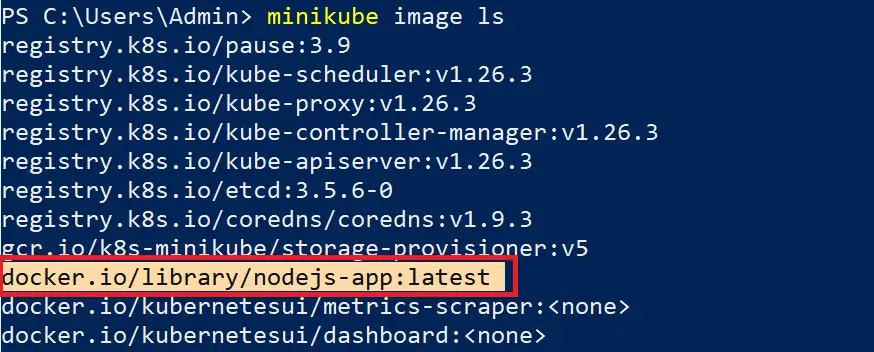
Now execute your deployment manifest, ensuring you replace image with your locally built image name:
kubectl create -f deployment.yml
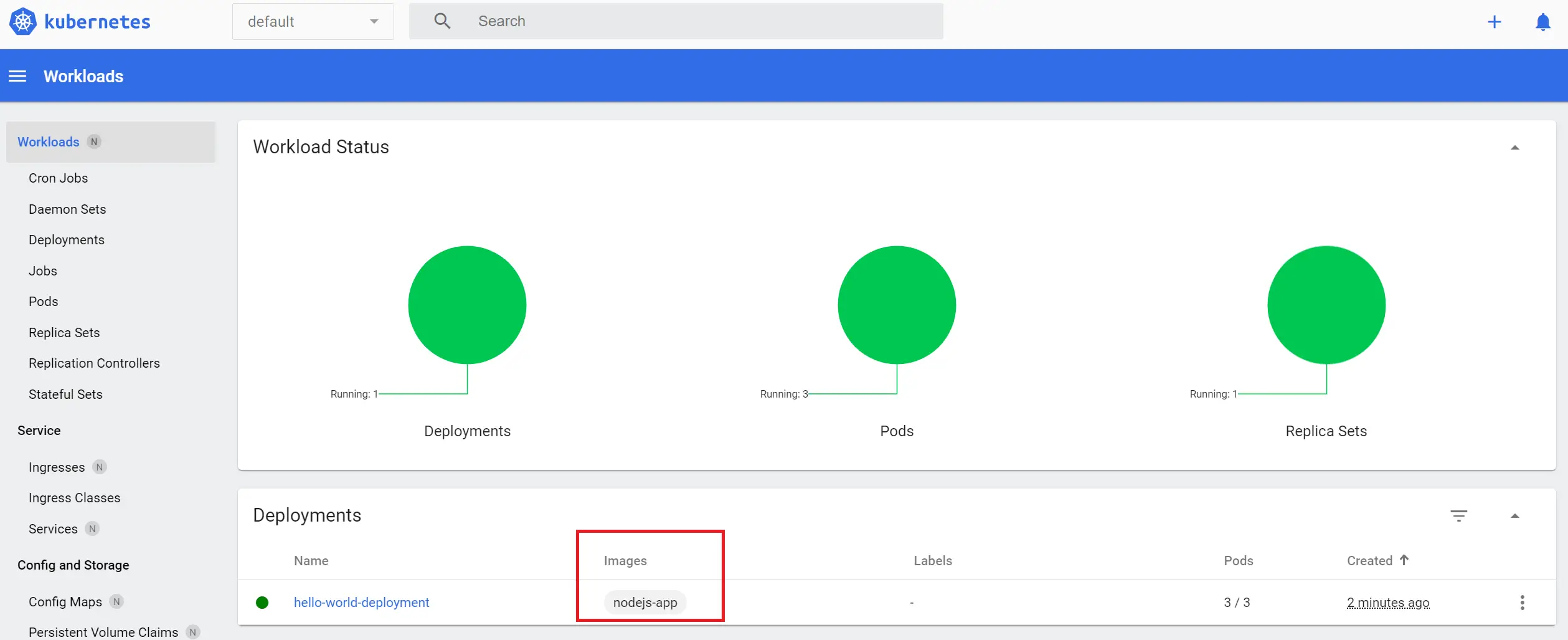
To investigate your cluster, open your Minikube bash board:
minikube dashboard
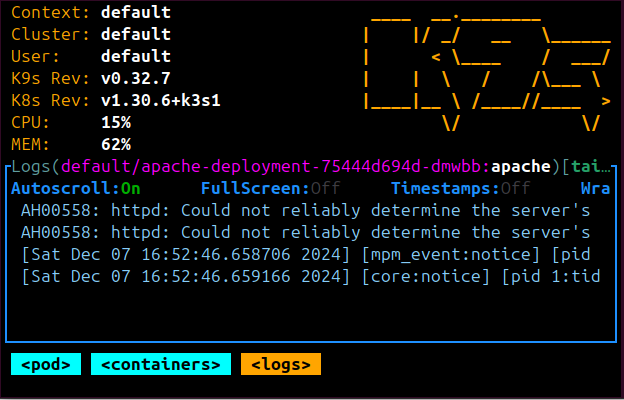
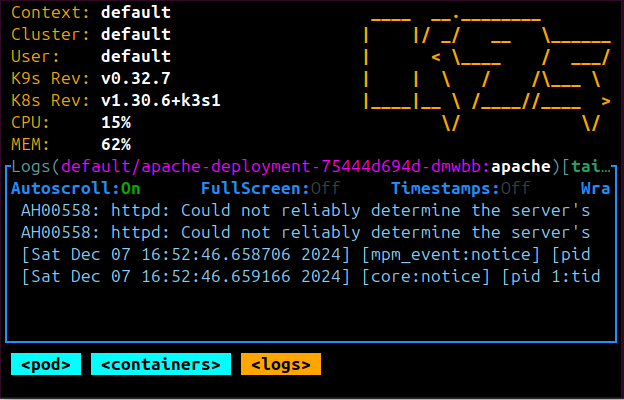
Your Local Minikube Docker Registry with Kubernetes Cluster should be running:
SOL 2: The Easiest way: Use Minikube Docker Registry Build Command
This should be the easiest way to Use the Kubernetes cluster locally using a Minikube local development docker registry.
Instead of using the docker build command, use the minikube build, and your Kubernetes local cluster will work like a charm:
minikube image build -t nodejs-app .
SOL 3: Bonus: Allow Minikube to Load Images to Local Repository
If all the above methods fail, this is a guaranteed solution here:
Once you run the docker build command to build your local docker image, use the following load command, and Minikube will Push your image to Kubernetes local clusters via Docker:
minikube image load -t node.js-app .
Conclusion
In this guide, you have learned:
- How to use Kubernetes local image repository
- Create a Minikube docker registry locally
- Use Minikube local registry to spin a local k8s cluster.
I hope this helped you take your Local Minikube Docker Registry with Kubernetes Cluster to the next level.