How to use docker php ext install and enable MongoDB Command
Posted November 20, 2023
PHP MongoDB extension adds functionalities to PHP for MongoDB database access within Dockerized applications. The MongoDB extension allows PHP and MongoDB in a Docker environment to create connections.
You will learn how to install your MongoDB PHP extension in your Dockerfile. If you are using Docker, you use the docker-php-ext-install or pecl install mongodb to get the right functions of MongoDB within Docker containers. At the same time, the command docker-php-ext-enable mongodb activates your MongoDB extension. This way the PHP app running on Docker can access MongoDB drivers.
This guide dives deeper into the ultimate MongoDB Docker container commands, docker-php-ext-install, pecl install, and docker-php-ext-enable mongodb. Dive in and explore the use of RUN docker-php-ext-install MongoDB Docker command to fine-tune extensions, an integral part of your PHP development workflow
Related: How to use RUN docker php ext install mysqli MySQL Command with Docker and How to use docker php ext install pgsql postgres Command
Step 1: Using MongoDB docker php ext install and pecl Commands with Dockerfile
Dockerfile is your base for packaging your PHP apps with Docker. It allows you to run any command PHP needs with Docker. In this case, PHP needs to access MongoDB. Therefore, you must use Dockerfile to install any extensions your app needs.
The docker-php-ext-install and pecl commands add PHP extensions on Docker. To Do that with MongoDB, you’ll add a RUN command within a Dockerfile as follows:
# Use an official PHP Apache runtime
FROM php:8.2-apache
# Enable Apache modules
RUN a2enmod rewrite
# Install MongoDB extension
RUN pecl install mongodb \
&& docker-php-ext-enable mongodb
In this case:
php:8.2-apacheis the version of PHP you are running (8.2). You can update it to your liking. However, ensure you have Apache. It will allow you to expose your PHP app to the web while running on Docker and fetch the latest version of available packages.RUN pecl install mongodbis equivalent to docker-php-ext-install mongodb. It will get the MongoDB extension installed on your Docker PHP containerdocker-php-ext-enable mongodbactivates the installed PHP extension. It’s from this point you will be able to use it along with your PHP code
Step 2: Using docker php ext (pecl), install MongoDB command with Docker Compose
You need to run two services at the same time, PHP and MongoDB. Docker Compose will spin them in one container so they can communicate and access your database. Docker Compose will run your Dockerfile and run the docker-php-ext-install, pecl install, and docker-php-ext-enable Mongodb commands to install these extensions.
In this step, you will create a docker-compose.yml file and add your PHP and MongoDB services as follows:
version: '3.9'
services:
php-apache:
build:
# Dockerfile path
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
# ADD local ./app directory to /var/www/html in the container
volumes:
- ./app:/var/www/html
ports:
- 8000:80
depends_on:
- mongodb
mongodb:
image: mongo:latest
ports:
- "27017:27017"
You will note that:
php-apachewill run based on your Docker file and Package your PHP source code withinapp/index.php. At this point, Docker Compose will reference the Dockerfile to RUN your docker-php-ext-install, pecl install, and docker-php-ext-enable mongodb.- A
mongodbservice will spin up MongoDB Docker instance. depends_ontells thephp-apachecontainer to use themongodbservice to add database connections.
Based on this example, you must have an app folder for your PHP files as follows:
php-mongdb/
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── docker-compose.yml
└── app/
└── index.php
Step 3: Creating PHP MongoDB Connection on Docker
You have a Docker file to package your PHP custom image and docker-compose.yml to spin up your needed container.
So, now to test if your docker-php-ext-install, pecl install, and docker-php-ext-enable MongoDB commands are working with Dockerized PHP, go to app/index.php and add MongoDB PHP connection test script as follows:
<?php
$mongoHost = 'mongodb';
$mongoPort = 27017;
try {
$mongoClient = new MongoDB\Driver\Manager("mongodb://{$mongoHost}:{$mongoPort}");
echo "Connected to MongoDB successfully!";
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "Failed to connect to MongoDB: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
The key things you need to note here are:
- PHP will try to create a connection to MongoDB using the URL
mongodb://mongodb:27017". MongoDB must be running on port 27017, as you added it on your docker-compose file. - At the same time,
mongoHostequalsmongodb. This must be the name of the service you use to run MongoDB. - Your Docker setup includes the MongoDB extension installed using the command pecl install (docker-php-ext-install) mongodb in the Dockerfile.
Step 4: Testing If MongoDB is working with PHP on Docker
Let’s now check the results of this setup. Go ahead and run the following docker-compose command to launch your PHP MongoDB containers:
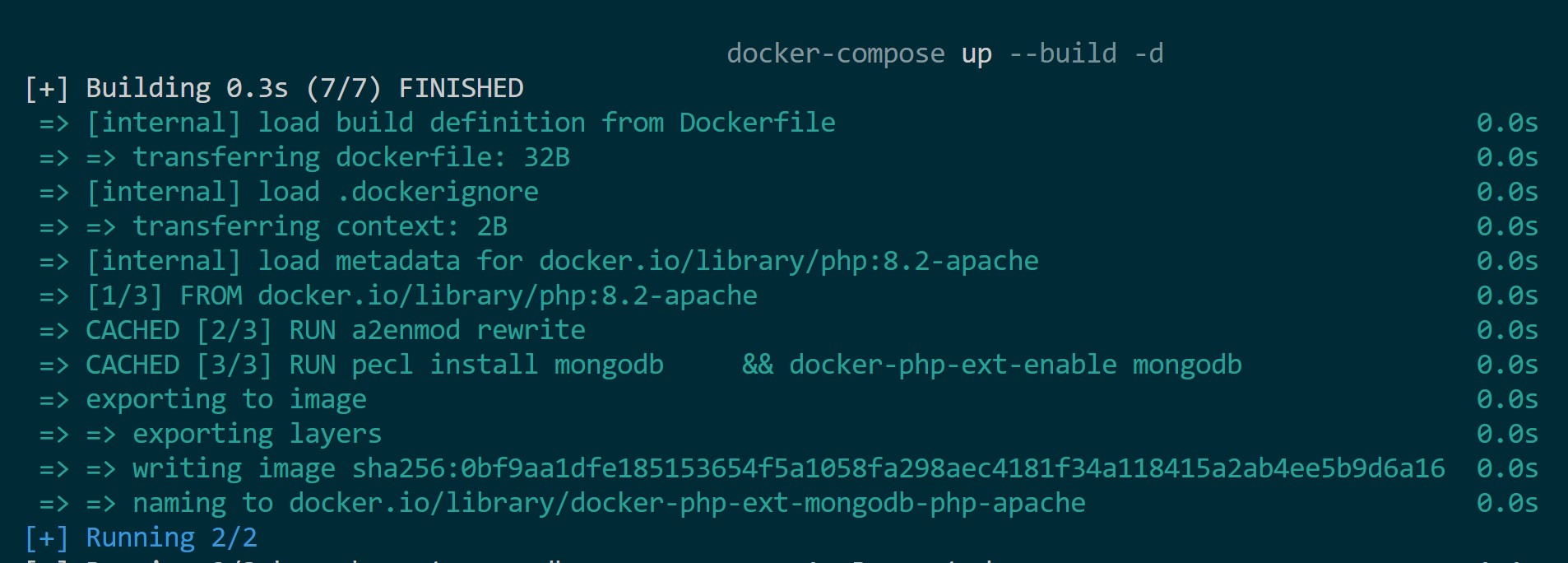
docker-compose up --build -d
Building images:
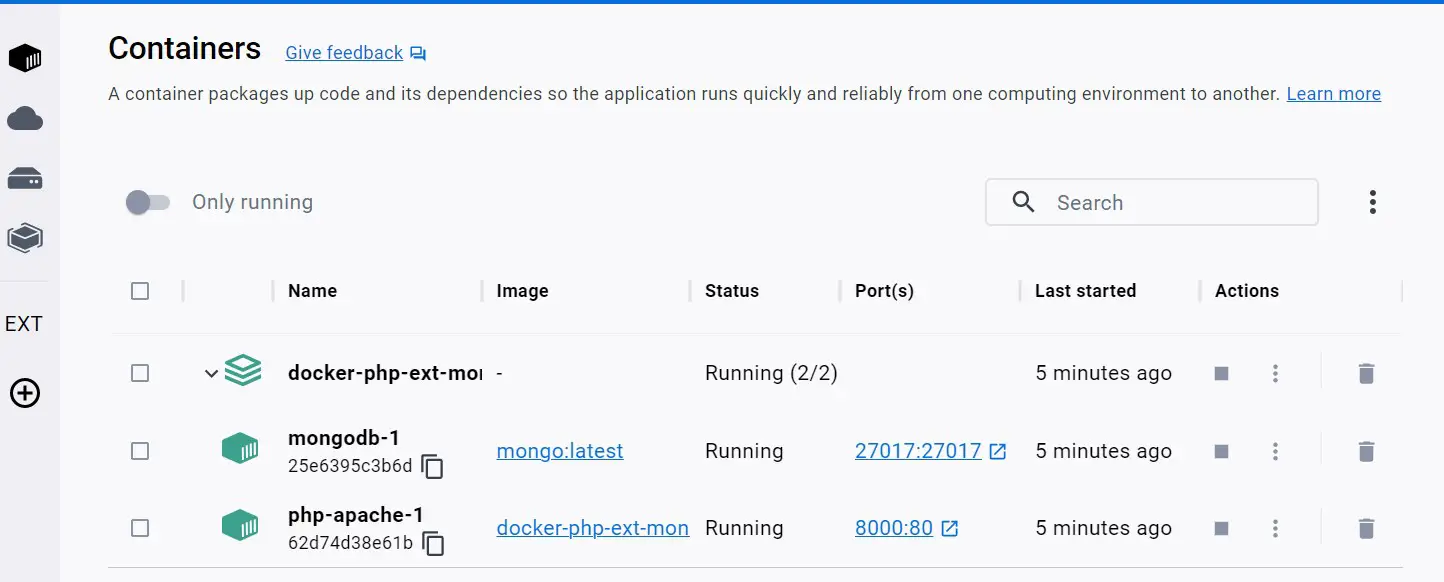
Check your running containers within your Docker:
Go to http://localhost:8000/ on your web browser. You should have a successful connection between PHP and your MongoDB database as follows:
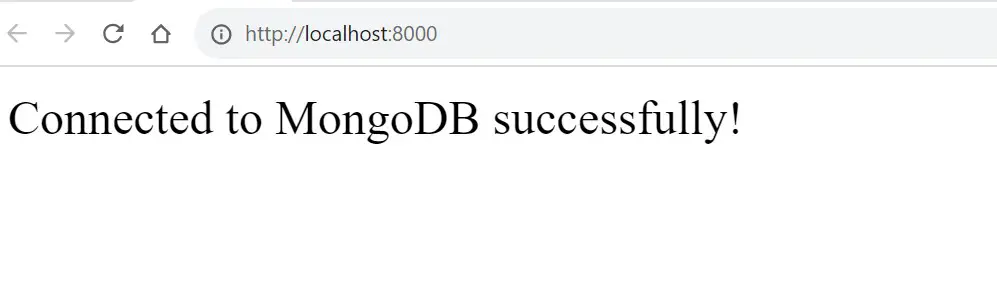
Your Dockerized PHP environment is running as you would expect and it is now and connected to the MongoDB database through the PHP Docker MongoDB extension.
Step 5: Accessing PHP Docker MongoDB Database using GUI
You have installed the PHP Docker MongoDB extension. And indeed, you can use it within your Dockerized PHP app. However, you want to access what is within your MongoDB database. You need a GUI to do that.
In this section, you will use Mongo Express as your GUI and access your DB. Go to your docker-compose.yml file and update your code as follows:
version: '3.9'
services:
php-apache:
build:
# Dockerfile path
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
# ADD local ./app directory to /var/www/html in the container
volumes:
- ./app:/var/www/html
ports:
- 8000:80
depends_on:
- mongodb
mongodb:
image: mongo:latest
container_name: mongodb
ports:
- "27017:27017"
environment:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: admin
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: pass
volumes:
- ./db_data/:/data/db/
- mongodb-data:/data/db
networks:
- mynetwork
mongo-express:
image: mongo-express:latest
container_name: mongo-express
ports:
- "8081:8081"
environment:
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME: admin
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD: pass
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_URL: mongodb://admin:pass@mongodb:27017/
networks:
- mynetwork
volumes:
mongodb-data:
db_data:
networks:
mynetwork:
Here, you are adding Mongo Express as your GUI. It needs to connect to your MongoDB database.
However, note that the database connection URI will change to mongodb://admin:pass@mongodb:27017/. This is because you have added a user who needs a username and a password to access MongoDB. In this case, the URI changes to mongodb://your_username:your_password@mongodb:27017/
At the same time, the URI must be updated on your PHP code as follows:
<?php
$mongoHost = 'mongodb';
$mongoPort = 27017;
try {
$mongoClient = new MongoDB\Driver\Manager("mongodb://admin:pass@mongodb:27017/");
echo "Connected to MongoDB successfully!";
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo "Failed to connect to MongoDB: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Now use the docker-compose command to relaunch your containers:
docker-compose up --build -d
Open http://localhost:8081/
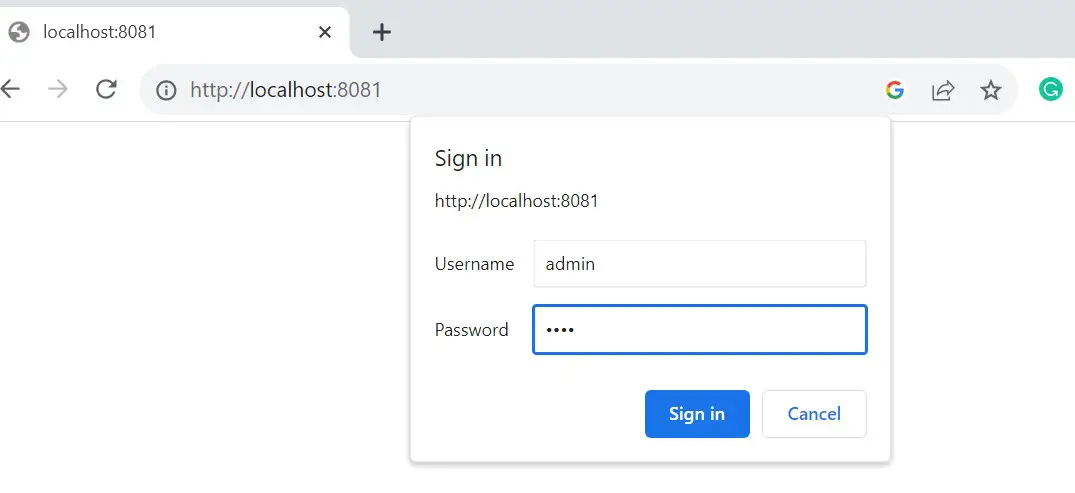
Use username as admin and password as pass to access your UI as follows:
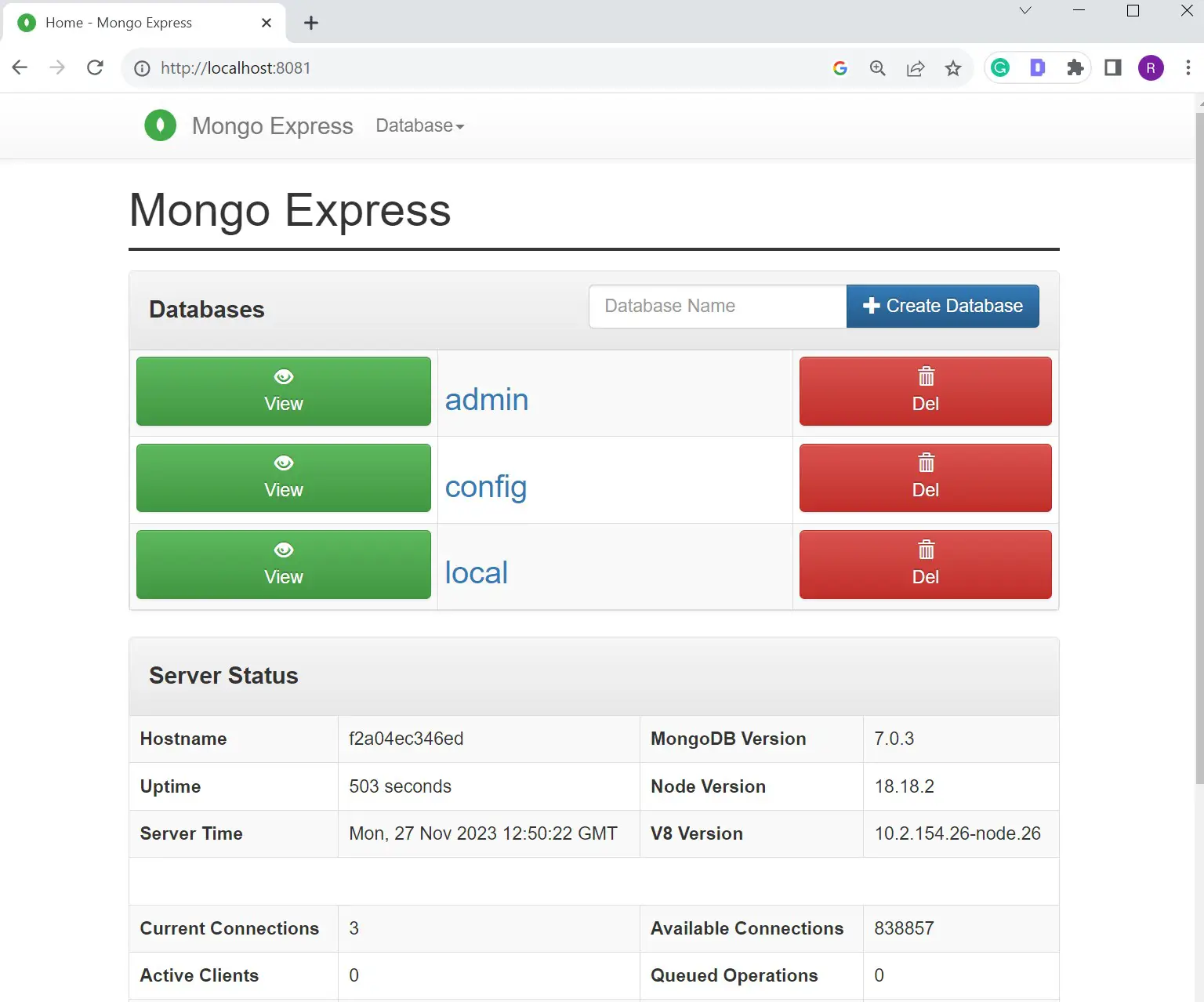
Conclusion
You have successfully used the docker-php-ext-install Mongodb command as your MongoDB extension for PHP within Docker. You can now confidently use the RUN docker-php-ext-install and enable Mongodb commands to integrate PHP and MongoDB in a Docker environment.