How to Install Portainer and Docker on Debian 9|10|11|12
Posted March 1, 2024
Portainer runs on any OS of your choice. This guide teaches how to install Docker and get it ready to run a Portainer service within Debian. All steps used here will get Portainer ready on Debian 9|10|11|12.
Along this Portainer Debian guide, you will learn:
- How to get Docker ready to run Portainer on Debian.
- Using Docker and Docker Compose to create a Portainer GUI within Debian.
- Using Debian Portainer UI to manage Docker environments.
- How to deploy the container to Docker using Portainer and Debian.
- How to add Certbot on Debian and add SSL certificates to only access Portainer on HTTPS.
Ready? Dive and learn How to Install Portainer and Docker on Debian.
Step 1: Requirement to Install Docker and Portainer on Debian
Docker will run Portainer. In this guide ensure:
- You have the basics of working with Docker.
- A Debian OS Ready.
- Ensure you have Hardware Requirements with at least 3GB Space and 2GB RAM before installing Portainer.
Step 2: Updating Debian Package Index
You need to Update your Debian system and have the latest package Index and security updates before running Portainer. Use the following commands:
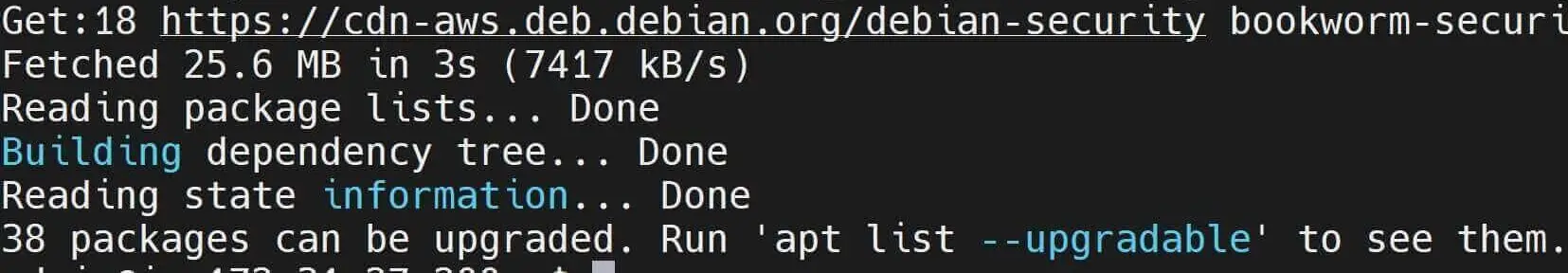
apt updateto update the local package index to reflect the latest changes in the repositories:
sudo apt update
- Use
apt upgradeto upgrade installed packages to their latest available versions:
sudo apt upgrade -y
Now, Debian should be ready to securely install Docker and Portainer
Step 3: Installing Docker For Portainer on Debian
Portainer runs within Docker. Portainer is only a UI to manage your Docker environments. This means you must have Docker installed. Check the following step to install it ON Debian:
- Install Required Dependencies
Docker needs specific packages for apt to use repositories over HTTPS and manage Docker dependencies. Install them as follows:
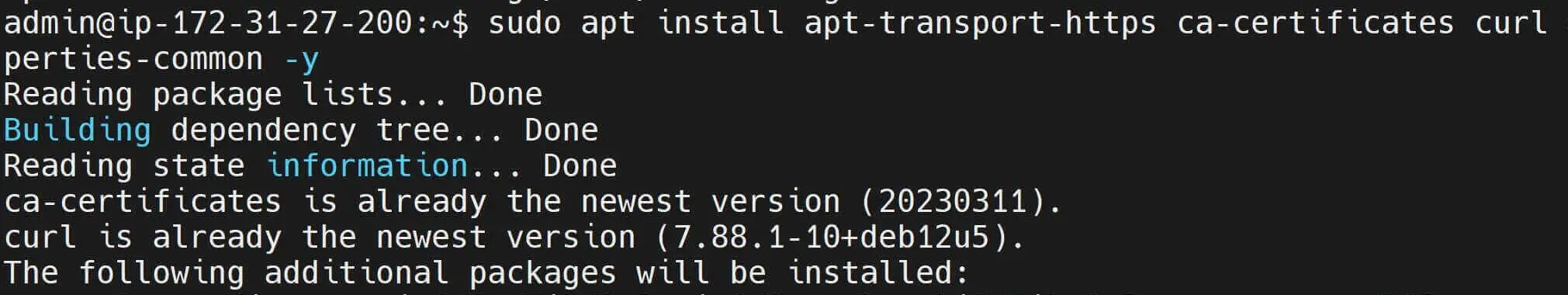
apt-transport-httpsso that apt uses HTTPS for secure communication with Docker repositories.ca-certificatesto add trusted certificates to establish secure connections.curlas a command-line tool.gnupg2GNU Privacy Guard to securely access Docker’s GPG key.software-properties-commonto add common utilities for managing software properties and repositories.
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg2 software-properties-common -y
- Next, Add Docker Official GPG Key, GPG key to verify the authenticity and integrity of Docker packages:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo apt-key add -

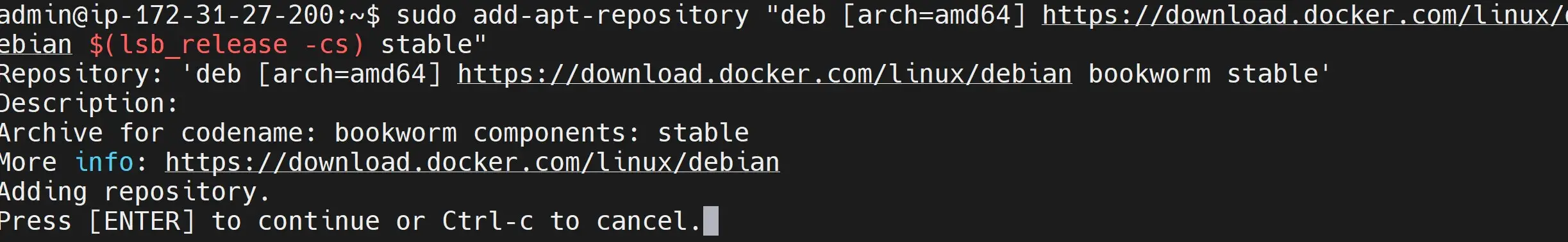
- Add Docker apt repository to your Debian package sources. This should use the Docker repository URL to add the latest Docker stable version:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
Make sure you click ENTER to continue.
- Now, install Docker Engine and associated packages like Docker Compose.
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y
- Next, verify Docker and Docker Compose are installed correctly
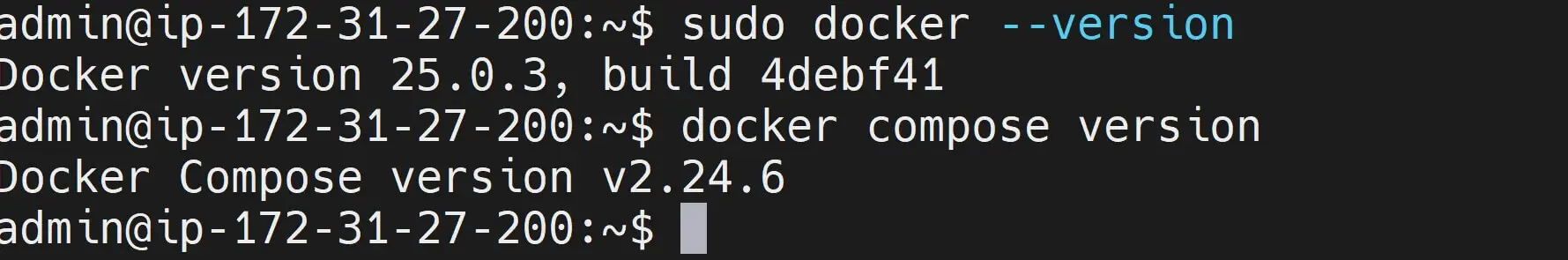
# Check versions
sudo docker --version
docker compose version
This command should display the installed Docker, and Docker Compose versions, confirming a successful installation.
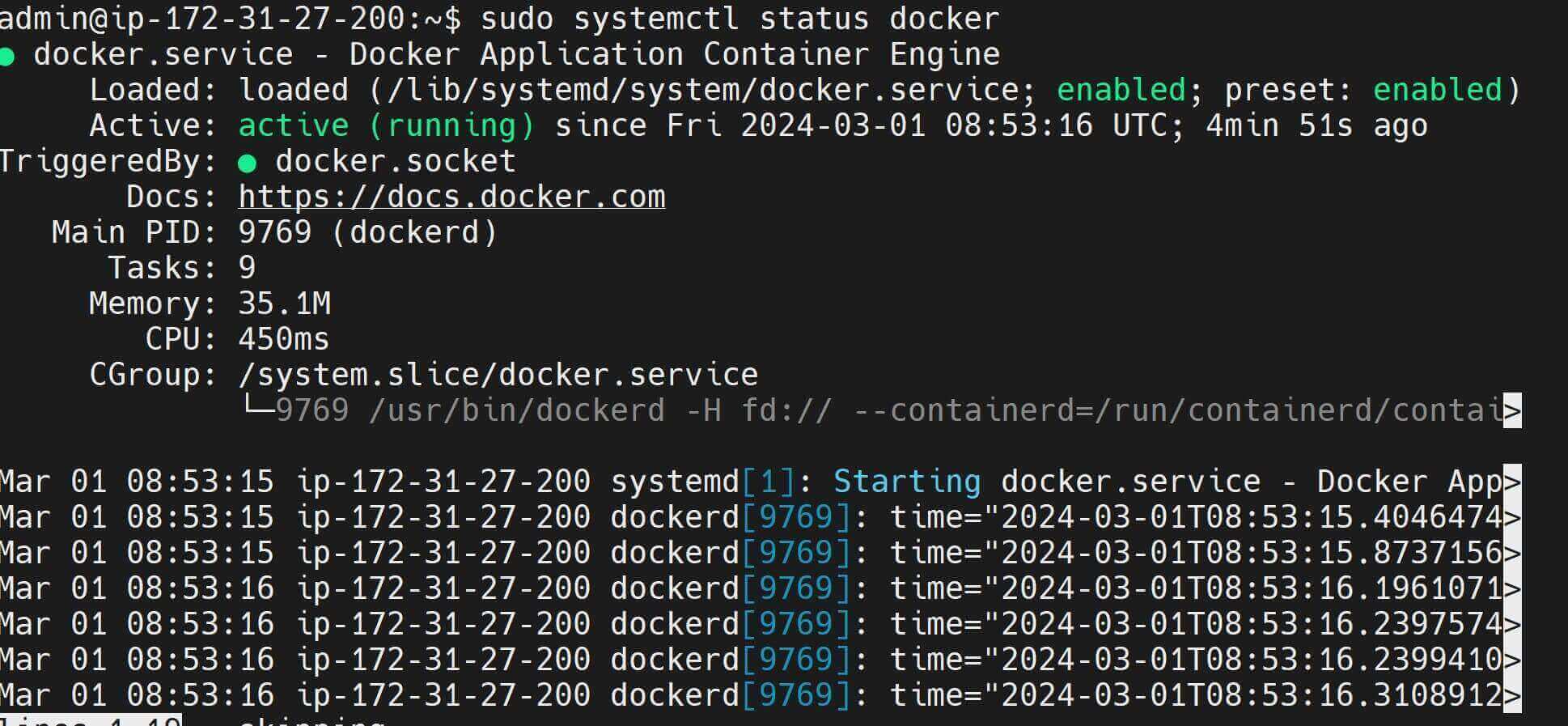
- Finally, Verify Docker is up and running using the
systemctlcommand:
sudo systemctl status docker
Step 4: Installing Portainer using Docker on Debian
You will learn two ways to get Portainer running on Debian. The first one is to use docker commands. Install Portainer as follows:
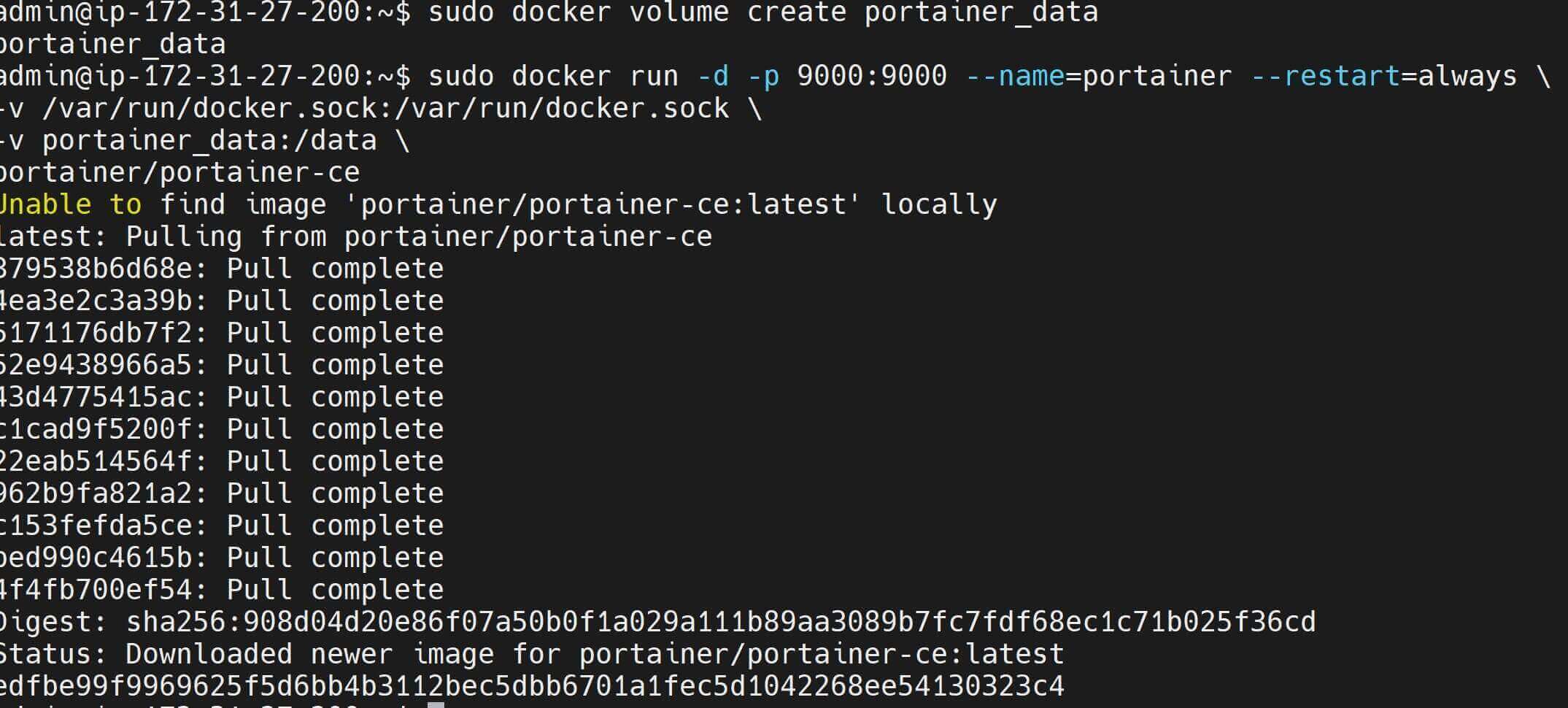
- Create a Docker volume for Portainer data persistence:
sudo docker volume create portainer_data
- Use Docker to Run a Portainer container:
sudo docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name=portainer --restart=always \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v portainer_data:/data \
portainer/portainer-ce
Step 5: Installing Portainer using Docker Compose on Debian
Another way to run Portainer on Debian is to use Docker Compose. Docker Compose uses a YAML file to configure Portainer. This way you define and orchestrate containers that make up the Portainer service. Now:
- Create a
docker-compose.ymlfile in your desired directory. - Open this file
nano docker-compose.ymland define Portainer with Compose as follows:
version: '3.9'
services:
portainer:
# Pull the latest image of Portainer Community Edition (CE)
image: portainer/portainer-ce:latest
# Add the container name
container_name: portainer
restart: always
# Expose and Map port 9000 to access Portainer
ports:
- "9000:9000"
volumes:
# This volume allows Portainer to interact with the Docker daemon
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
# This volume holds Portainer configuration and other data
- portainer_data:/data
volumes:
# Add the portainer data volume to persist changes
portainer_data:
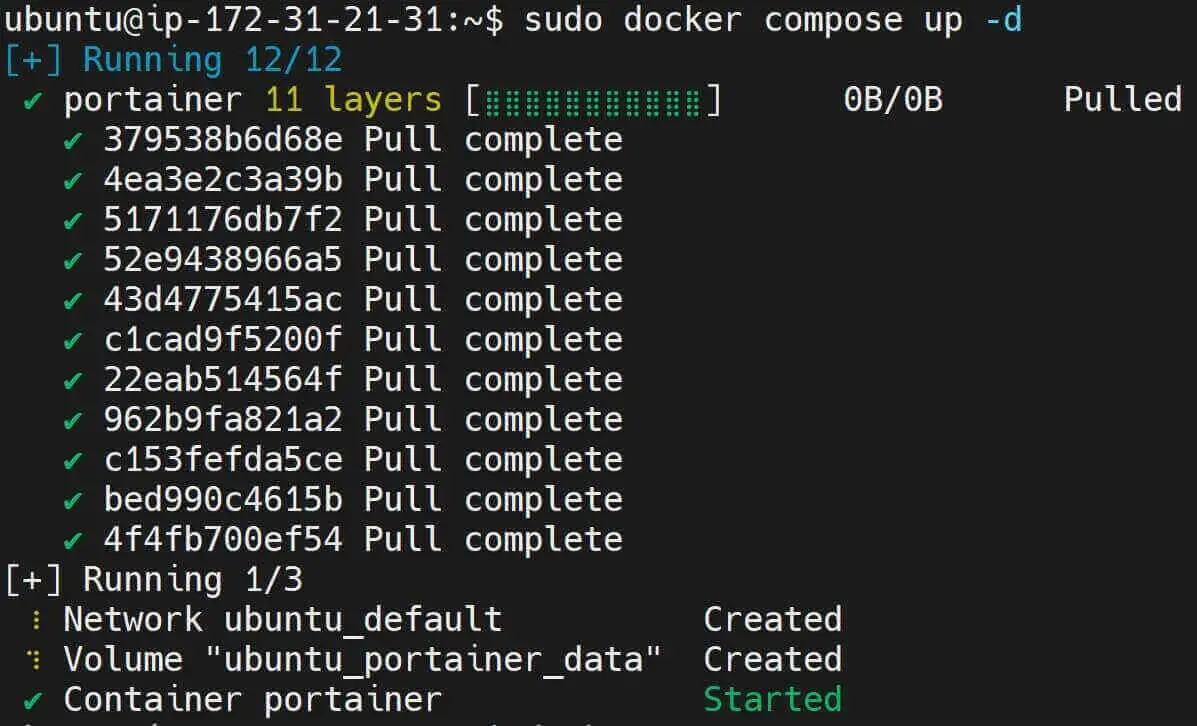
- Next, use the following docker-compose compose command to run your container:
sudo docker compose up -d
Step 6: Accessing Portainer UI on Debian
You should use only one of the above methods to run Portainer. Check that Debian is running your Portainer on port 9000:
sudo docker ps
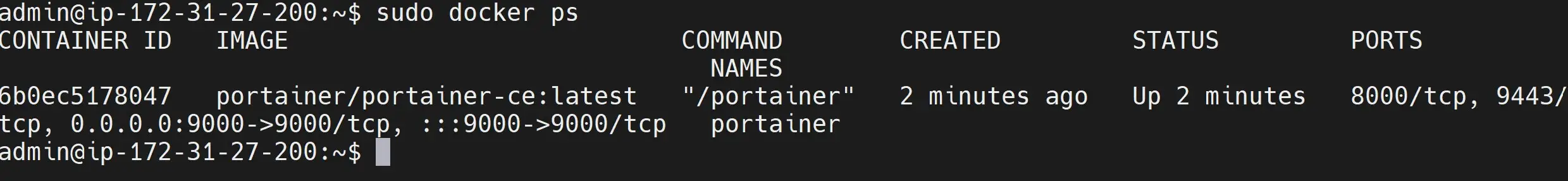
This means you should now open http://your_server_ip:9000 in the web browser to access the deployed Portainer server:
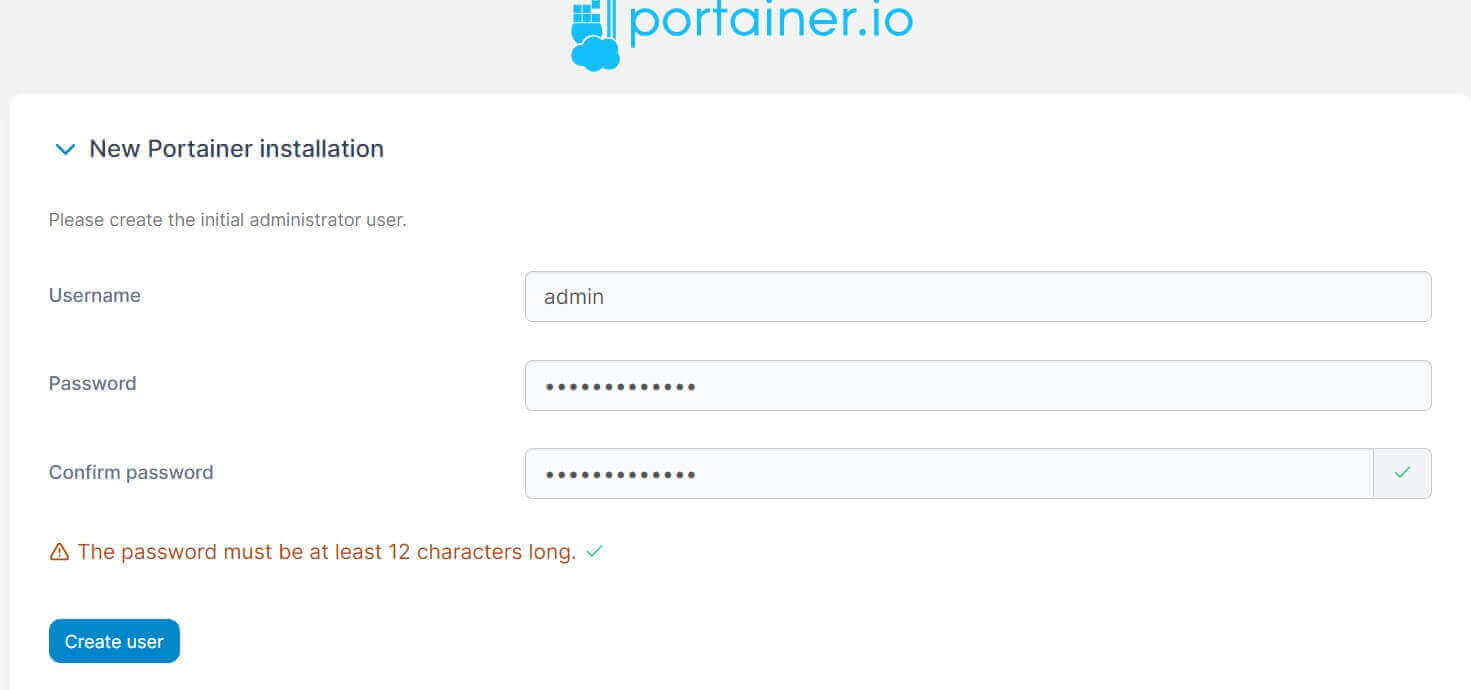
At this point, create a User and add login details:
If you get an error as follows:

Restart the container and everything will work as fine?
sudo docker restart portainer
Here is the first view of your installed Portainer Debian UI wizard:
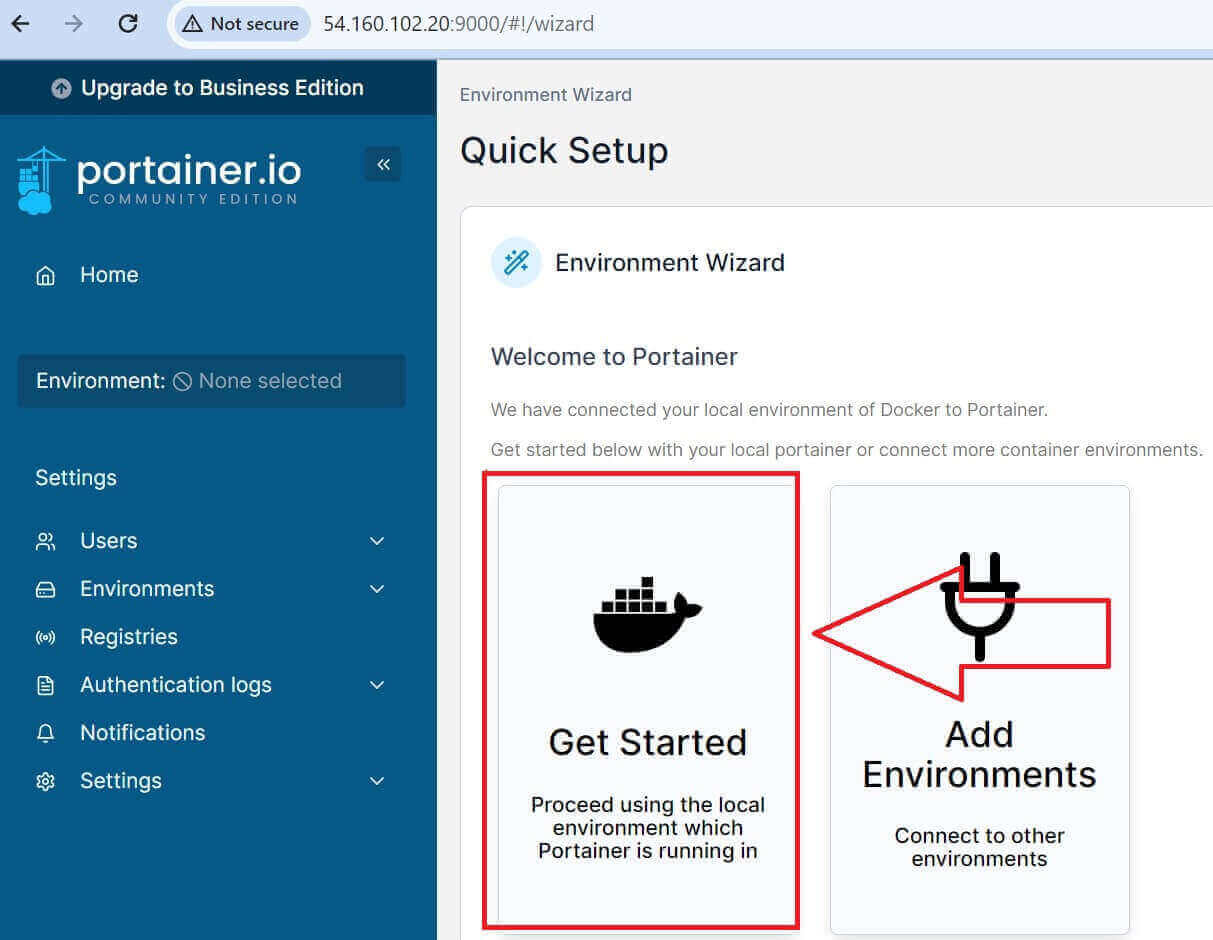
Step 7: Managing Docker Containers With Portainer
On the quick setup page, You should have a Docker environment that you want Portainer to manage. In this example, you will use a locally installed Docker environment.
- Click on the Get Started box.

- This should load the local Docker configurations on your machine:
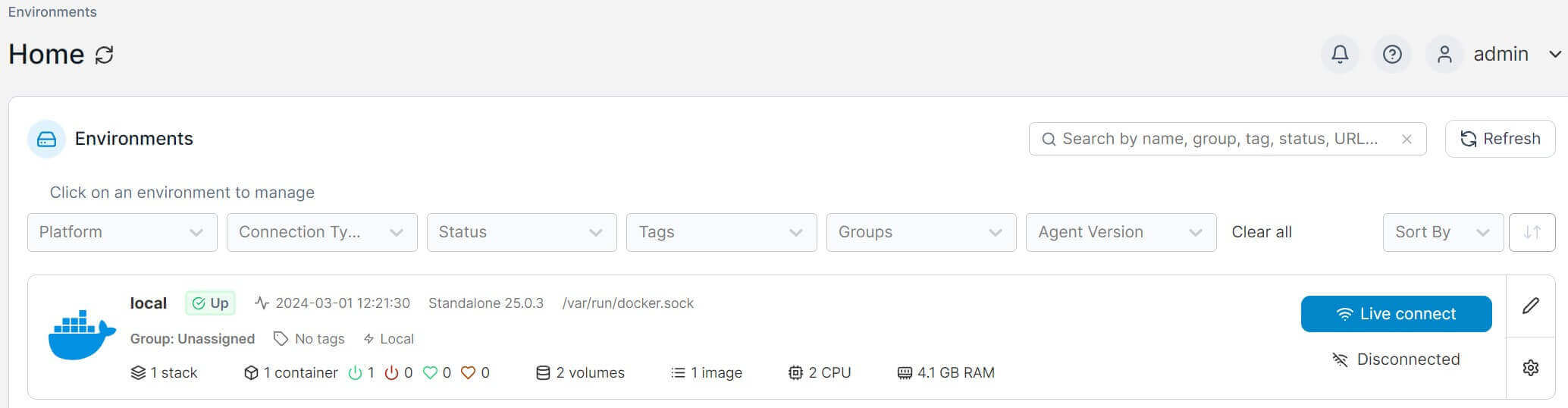
- To get a detailed view, click local and you will have a UI for all Docker resources:
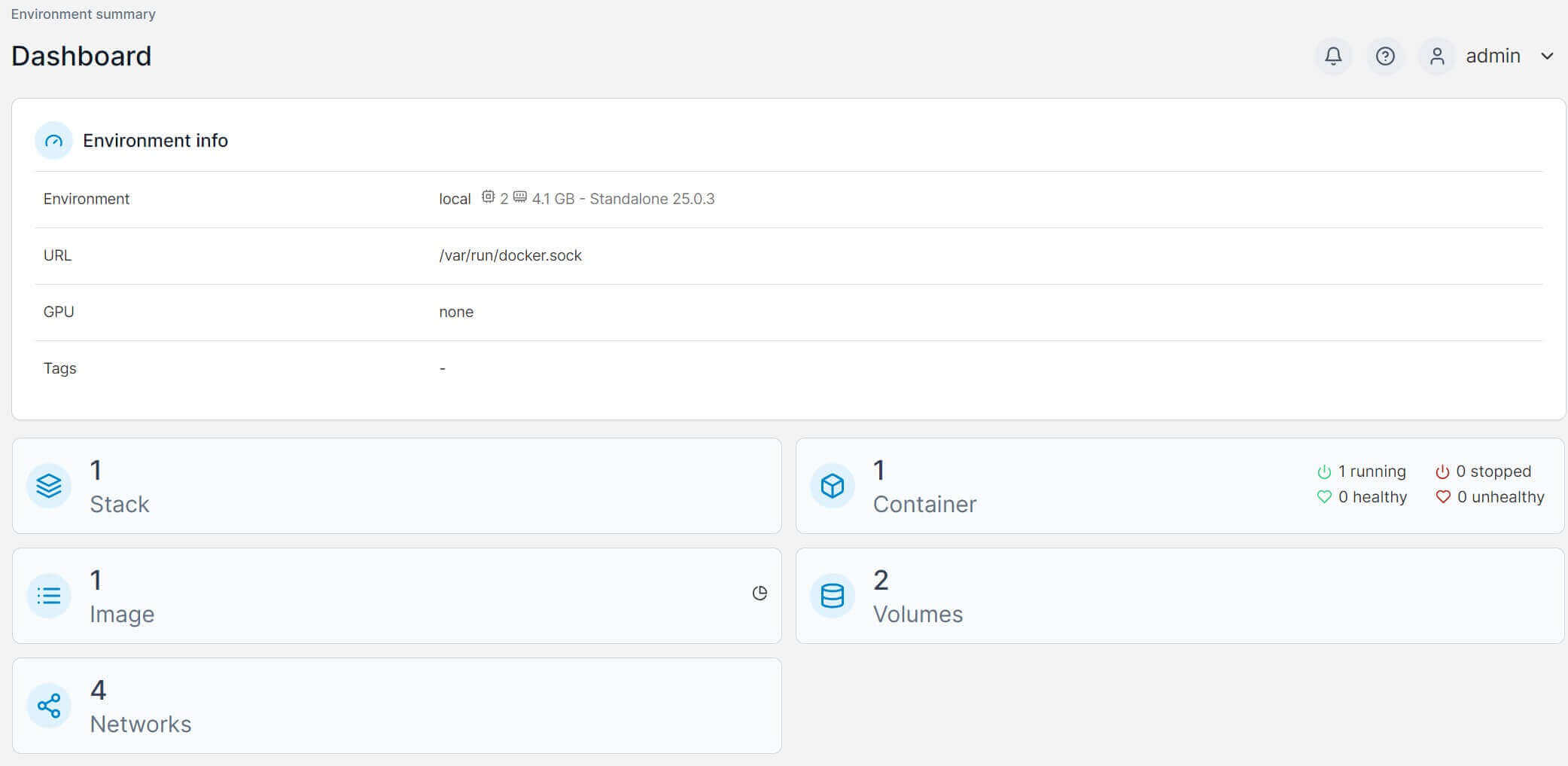
Step 8: Deploying Containers to Debian and Docker using Portainer
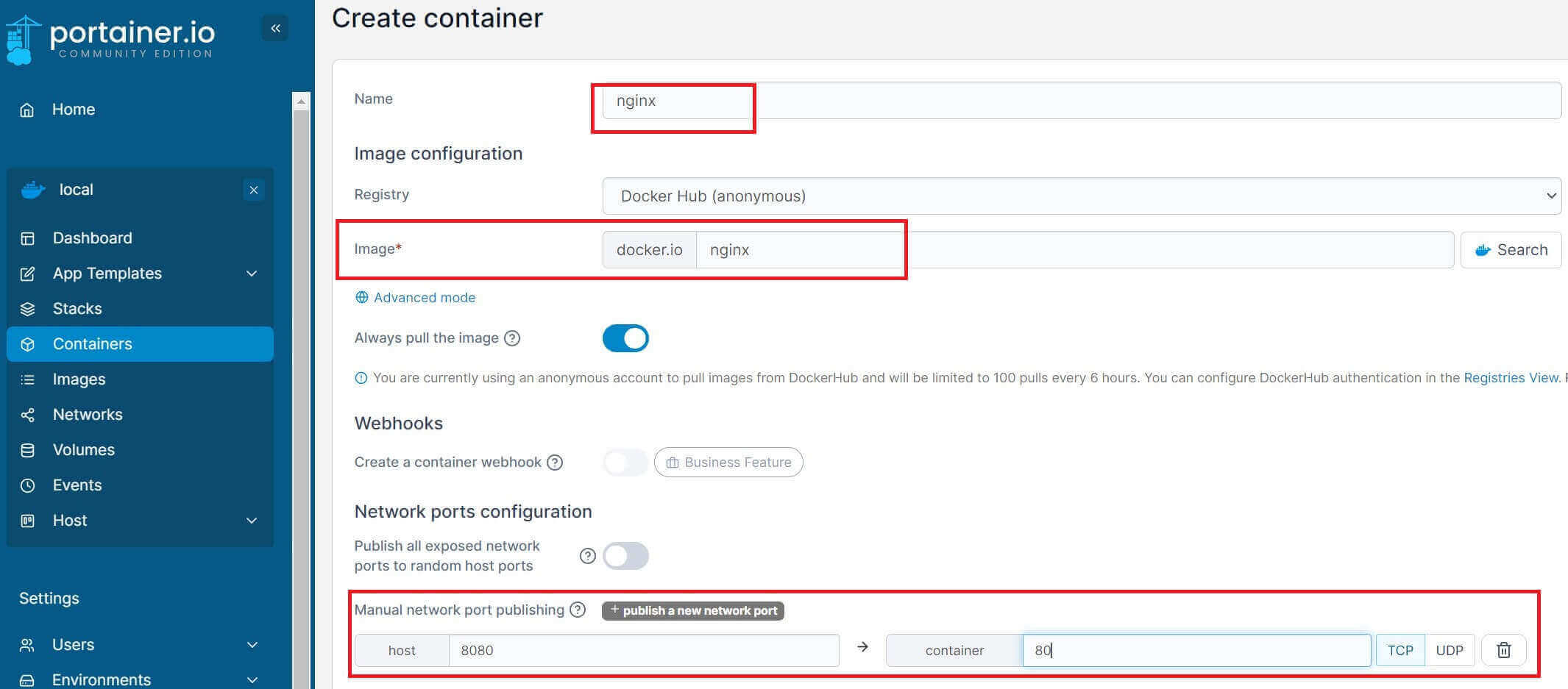
If you want to dive deep and deploy a container in this setup, you will navigate to Containers sections and create a Add a new container as follows:
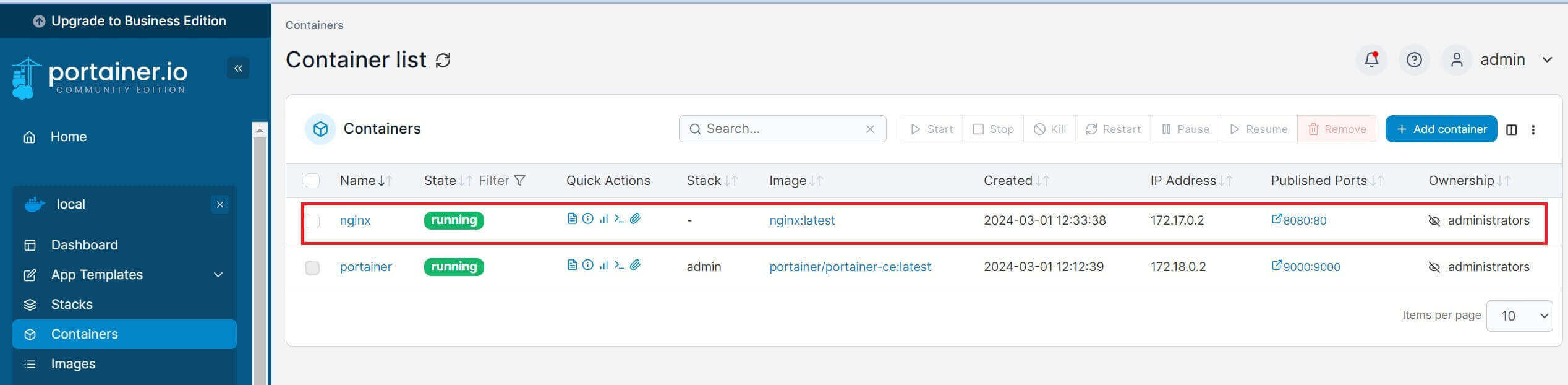
You will then deploy this container and you should have it ready on Portainer:
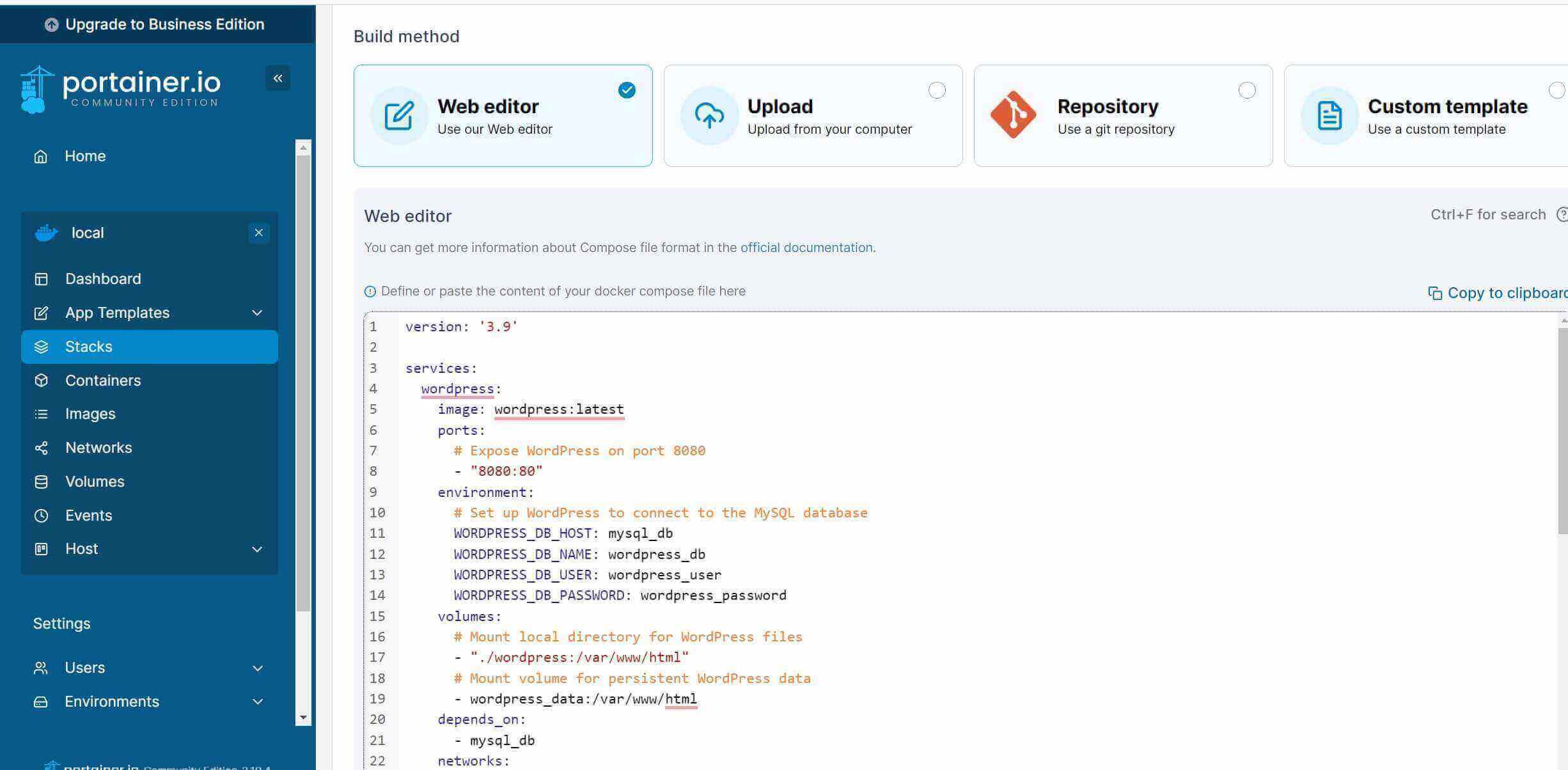
A better way is to use Docker Compose if you have a stack of containers. In this case, you will go to Stacks, Add Stack and use Portainer web editor:
This How to Install and Run WordPress with Portainer guide perfectly shows you how to use the Portainer stack feature in deeper detail.
Step 9: Accessing Portainer with HTTPS SSL Cert On Debian
What if you want to access Portainer with HTTPS using SSL/TLS certificates on Debian?
You’ll need to set up a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to handle HTTPS requests and terminate SSL/TLS encryption. Check these steps:
If you are not using domain names, check this guide for other Portainer HTTPS options.
- Install SSL/TLS Certificates for your domain using Certbot:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
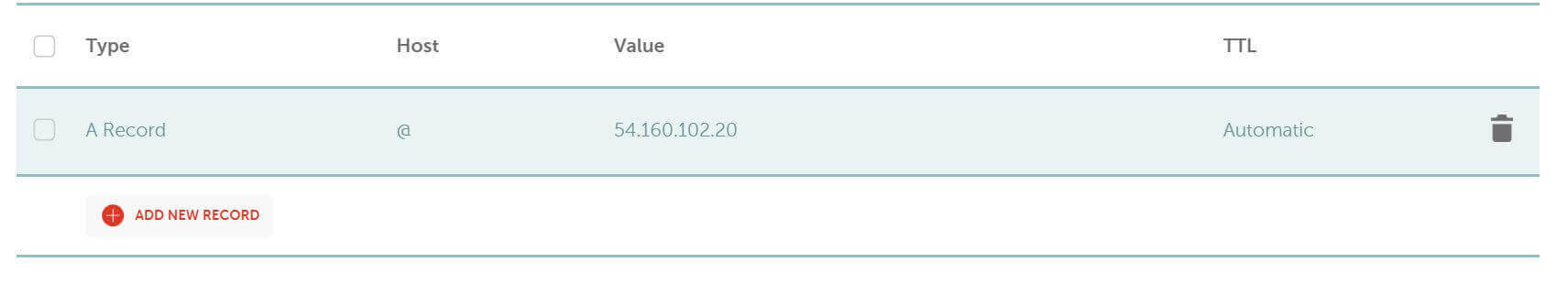
- Add a DNS A record to your domain name pointing to your_server_ip:
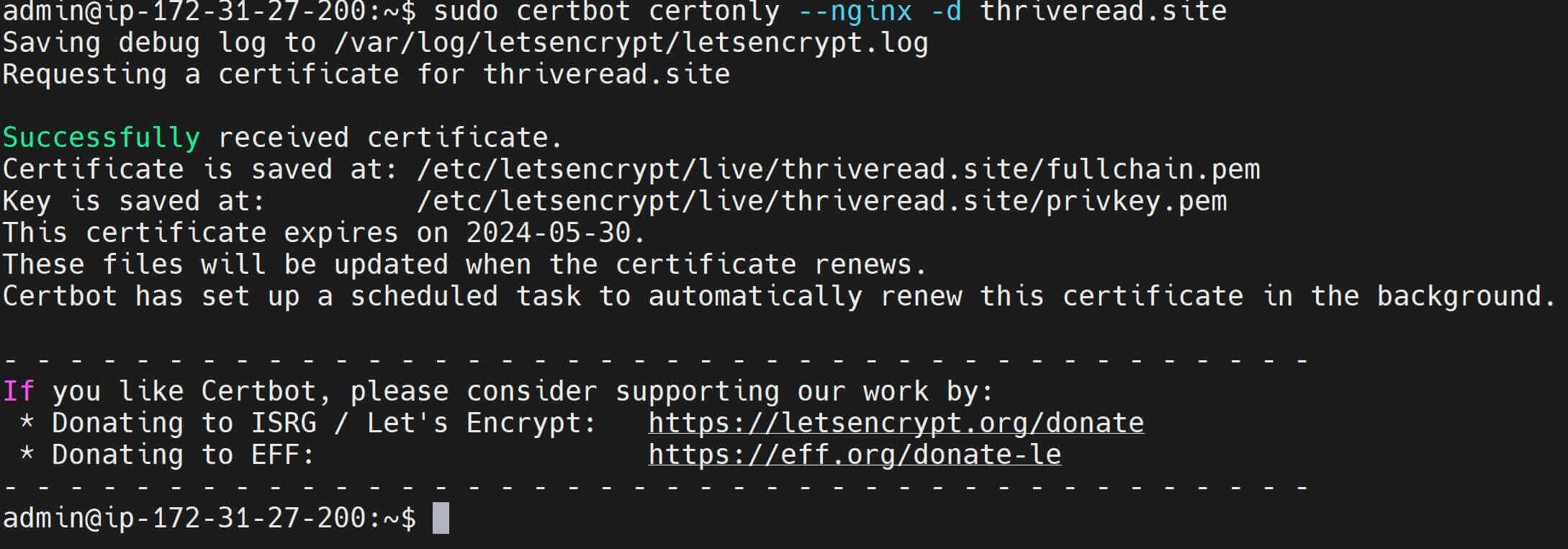
- Get SSL/TLS certificates for your domain (add email and other details when prompted):
sudo certbot certonly --nginx -d your_domain.com
- Install Nginx as a Reverse Proxy:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
- Create a new Nginx configuration file for Portainer:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/portainer
- Create and configure the Portainer domain name with Nginx Reverse Proxy:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name your_domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_pass http://your_server_ip:9000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
- Use this Nginx configuration:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/portainer /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
- Test the configurations and Reload Nginx to apply the changes:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginx

Nginx should now handle the HTTPS requests and forward them to Portainer running on port 9000.
You might need a few minutes to ensure propagation.
Now use https://your_domain.com to access Portainer and log in using previous details:

And there you have Nginx will handle the HTTPS requests and forward them to Portainer running on port 9000:
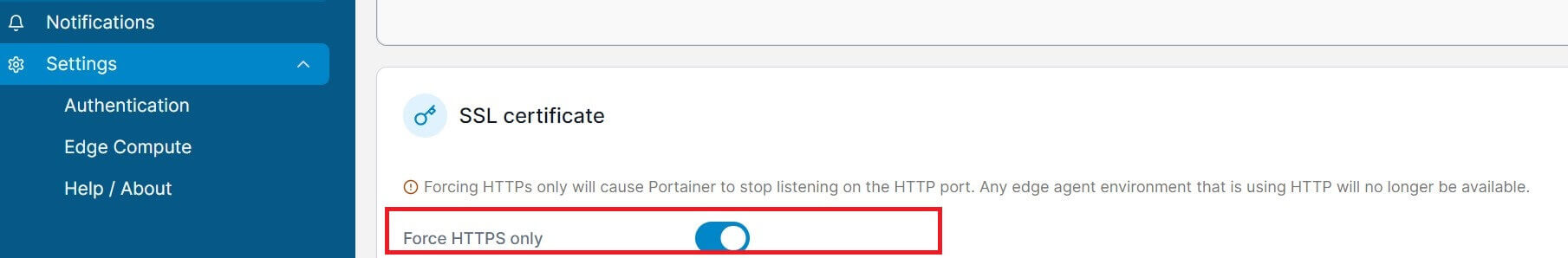
Now, you need to force Portainer to use HTTPS. Go to Portainer settings and Force HTTPs only:
If you want to add an Automatic Certificate Renewal with Certbot add a cron job as follows:
- Install cron:
sudo apt-get install cron -y
- Certbot should have already set up a cron job during installation. Verify it:
sudo crontab -l
- If renewal is not present, add it manually:
sudo crontab -e
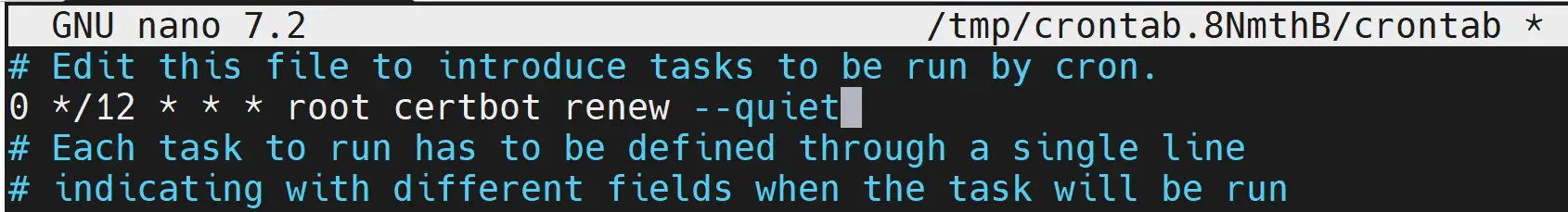
- Renew the certificates twice a day:
0 */12 * * * root certbot renew --quiet
You have successfully installed Portainer and Docker on your Debian server. Portainer is accessible via HTTPS with SSL/TLS encryption on Debian. You have now learned:
- How to get Docker ready to run Portainer on Debian.
- Using Docker and Docker Compose to create a Portainer GUI within Debian.
- Using Debian Portainer UI to manage Docker environments.
- How to deploy the container to Docker using Portainer and Debian.
- How to add Certbot on Debian and add SSL certificates to only access Portainer on HTTPS.


