Install and Run Kubectl on Linux|Ubuntu 20.04|22.04|18.04
Posted March 4, 2024

This Guide teaches you how to install and set up Kubectl to run Kubernetes commands on a Linux Ubuntu server 20.04|22.04. Before using Kubernetes ubuntu server must have Kubectl command line tools well configured. You will all the steps you need to install Kubernetes’ command-line tool Kubectl on Ubuntu.
Kubectl performs operations on Kubernetes clusters, like deploying applications, managing resources (pods, services, deployments, etc.), inspecting cluster state, and executing commands inside containers. To get Kubectl on Ubuntu, you will learn:
- How to install Kubectl on Ubuntu using Snap.
- Using apt package manager and Kubernetes apt repository to install Kubectl on Ubuntu server 20.04|22.04.
- Install Ubuntu Kubectl binary using curl from the Kubernetes GitHub repository.
- Kubernetes Kubectl shorthand command you need to know and run on your Ubuntu server.
- Learn Ubuntu Kubectl commands cheat sheet.
- How to Install Kubernetes on Ubuntu.
- Uninstalling Kubectl from Ubuntu
Related:
Ready? Now dive in, Install, and Run Kubectl Linux|Ubuntu 20.04|22.04 like a Pro
Step 1: Requirements to Run Kubectl on Linux Ubuntu Server
Before setting up your Kubectl command-line tool, ensure your Ubuntu machine has:
- Internet access or access to the Ubuntu Kubernetes cluster you want to manage with Kubectl
- Kubectl is lightweight. However, its goal is to run Kubernetes. Therefore, Ubuntu must have at least a single CPU core available, 20GB of free disk space, and a minimum of 2GB of RAM.
Step 2: Update the Package index
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Step 3: Installing Kubectl on Ubuntu using Snap
Snap allows Ubuntu to package apps and all their dependencies into a single, self-contained package called a snap. The good thing about Snaps is, they are isolated from the rest of the system through containerization. This way, they have limited access to system resources, enhancing security.
To use Snap and get Kubectl ready on Ubuntu:
- Install Kubectl using Snap:
sudo snap install kubectl --classic
This command should get Kubectl on your Ubuntu from the Snap Store:

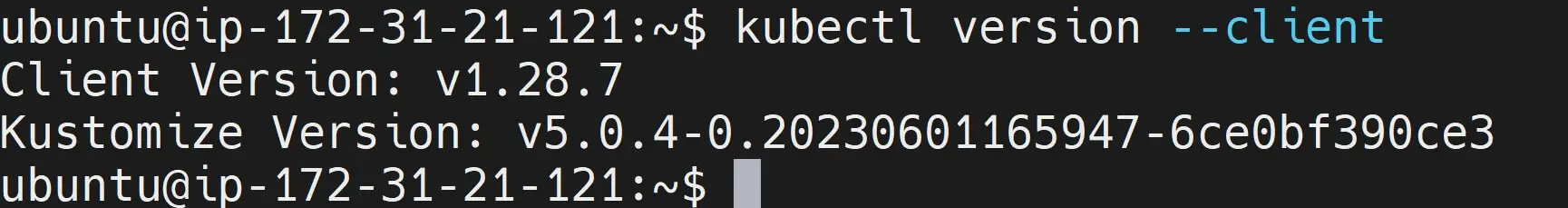
- Check the installed Kubectl to verify if the Kubectl binary is available on your Ubuntu system:
kubectl version --client
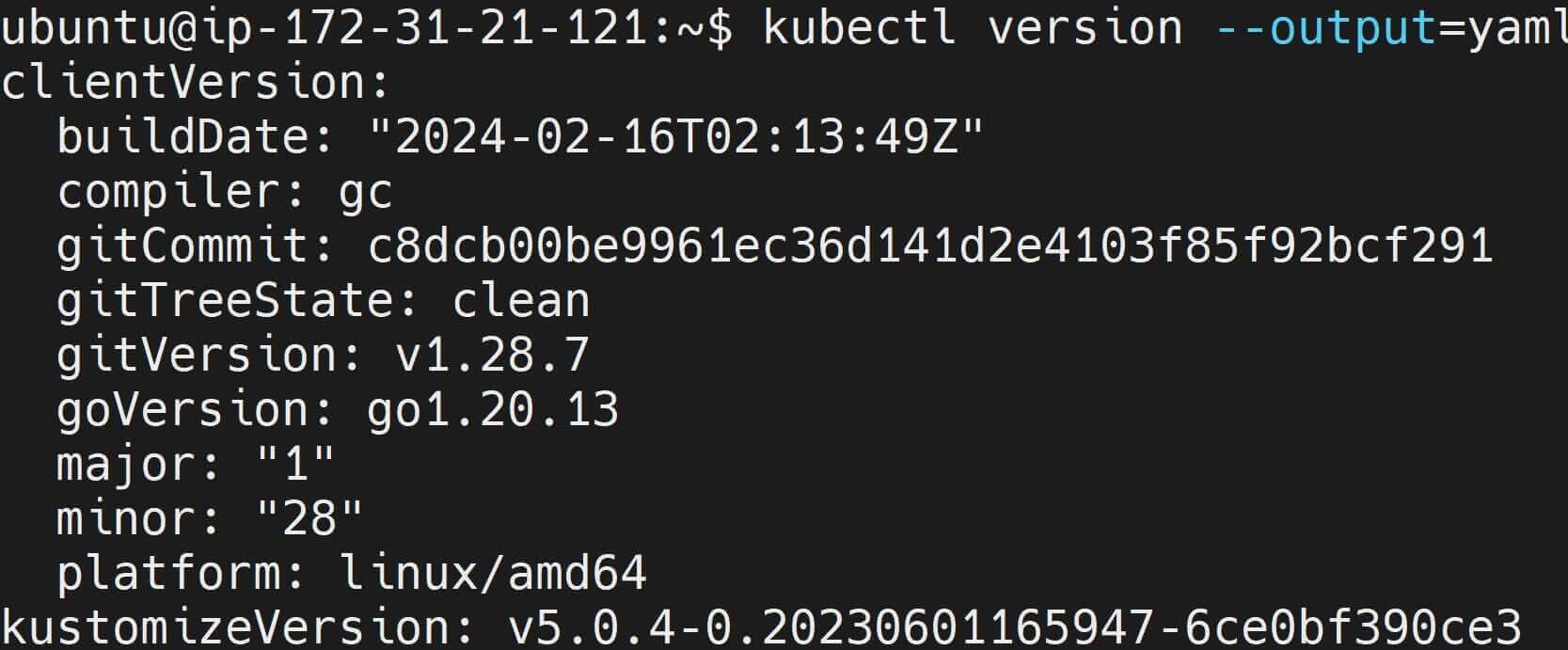
Still, you can use the above command and check the Kubectl Ubuntu YAML:
kubectl version --output=yaml
Step 4: Install Kubectl on Ubuntu 20.04|22.04 using Kubernetes apt Repository
Kubernetes apt repository maintains Kubernetes-related packages like Kubectl for distributions like Ubuntu. To access them, you use the apt package manager as follows:
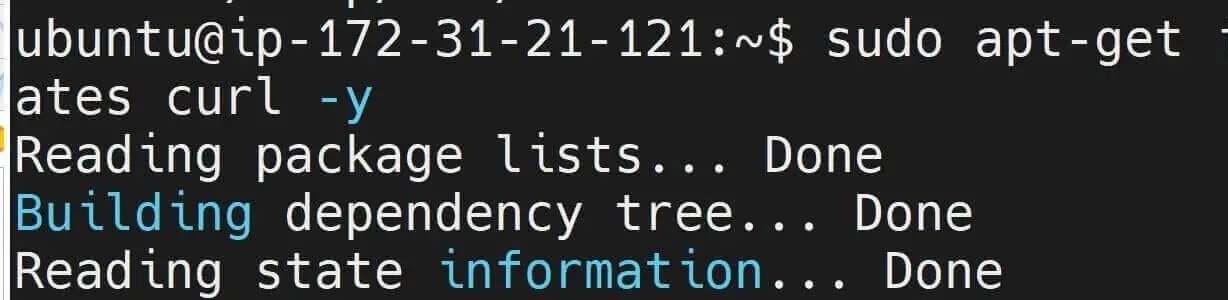
- Install packages that Kubernetes apt Repository needs to get Kubectl ready on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl
- Add a Public signing key to let Ubuntu add Kubernetes apt Repository to the sources in a secure way:
curl -fsSL https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
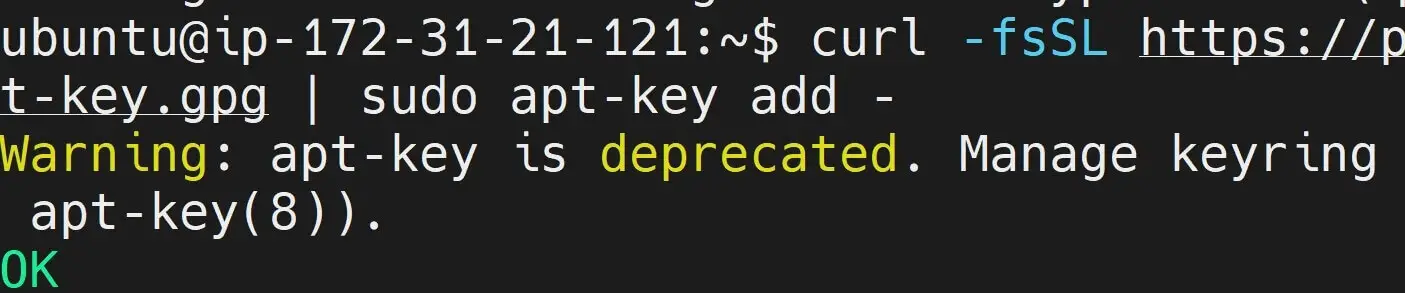
Recommended: Because apt-key is deprecated, the public signing key for the Kubernetes package repositories instead:
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
However, if you are using older than Debian 12 and Ubuntu 22.04 versions, you must create a /etc/apt/keyrings folder with curl:
sudo mkdir -p -m 755 /etc/apt/keyrings
You can then proceed and run the above public signing key for the Kubernetes package repositories command.
- Now add the Kubernetes apt repository to Ubuntu:
echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-impish main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
If you are using Ubuntu 22.04, replace xenial with impish:
echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-impish main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
Recommended:
If you used a public signing key for the Kubernetes package repositories:
echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
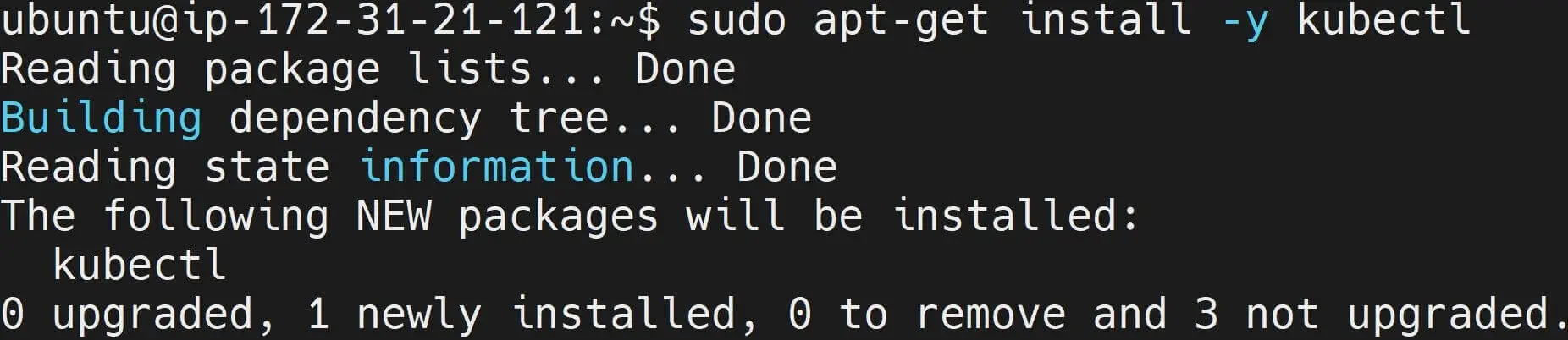
- Install Kubectl from the above Ubuntu repository source:
# Update the package index again
sudo apt-get update
## Install kubectl
sudo apt install kubectl -y
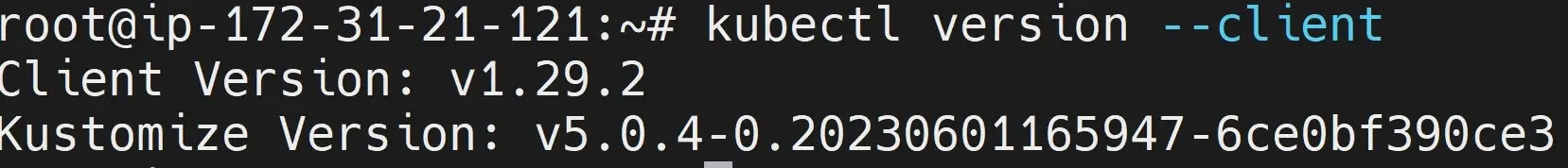
Finally, check the available installed Kubectl Ubuntu version:
kubectl version --client
Step 5: Install and Run Kubectl on Linux|Ubuntu 20.04|22.04 with Curl
These steps will install the Ubuntu Kubectl binary using curl from the Kubernetes GitHub repository.
In this case, you will install the Kubectl binary using curl and download the binary from the official Kubernetes GitHub repository. as follows:
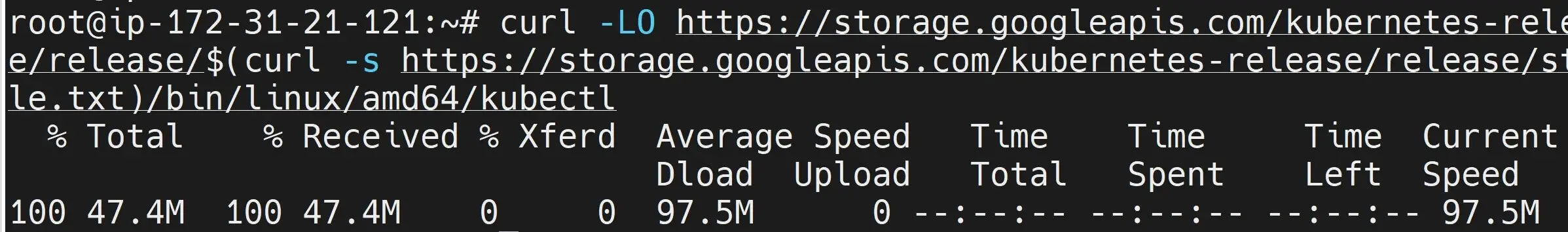
- Use Curl to Download the Kubectl Ubuntu binary:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
Note: this command is downloading the latest version of Kubectl for Linux (
amd64architecture). Replacelinux/amd64with your Linux Ubuntu distribution.
- Use
chmodto ensure the downloaded binary executable:
chmod +x ./kubectl
- Your Kubectl binary should be on your Ubuntu
/usr/bin/kubectlPATH. Run the following command and add binary to a directory in your PATH:
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl
If you are using the PATH environment variable as /usr/local/bin, replace the above command as such:
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Check the version of kubectl that you’ve just installed.
kubectl version --client
Step 6: How Ubuntu Configure Bash Auto-completion for Kubectl
To add Kubectl command auto-completion, you will press the Tab key to complete Kubectl commands, options, and resource names.
This way, Ubuntu will support auto-completion support for Kubectl commands in the Bash shell.
Run the following command to set it up:
## Autocomplete permanently
echo 'source <(kubectl completion bash)' >> ~/.bashrc
## Autocomplete into the current shell
source <(kubectl completion bash)
If you are using kubectl auto-completion for Zsh, add the following line to your ~/.zshrc file:
source <(kubectl completion zsh)
For example, use you Type kub then press the tab, Bash shell should auto-complete kubectl
Other usability settings you can add are:
- Apply changes to the current session:
This is where you need to reload the .bashrc file. This should apply the changes made in steps 3 and 4 to the current Bash session:
## Autocomplete into the current shell
source ~/.bashrc
## Autocomplete permanently
echo '[[ $commands[kubectl] ]] && source <(kubectl completion zsh)' >> ~/.zshrc
- Allow Kubectl to use the default namespace:
For more convenience for day-to-day use, alias k for Kubectl completes Kubectl commands by pressing Tab.
At the same time, the k alias makes use of the default namespace for Kubernetes operations:
echo 'alias k=kubectl' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'complete -F __start_kubectl k' >> ~/.bashrc
Step 7: Using Kubectl and Kubernetes on Ubuntu
Once you have the Kubectl installed, you can install Kubernetes with these steps:
Check this guide to get a lightweight K3s Cluster Running on your Ubuntu machine:
Step 8: Common shorthand Commands for Kubectl on Ubuntu
To get started on your Kubernetes management using Kubectl, the following will be the day-to-day Kubectl command that you will use on your Linux Ubuntu server. These should be the Kubectl commands cheat sheet:
- Get Resources:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl get pods |
List all pods |
kubectl get deployments |
List all deployments |
kubectl get services |
List all services |
kubectl get nodes |
List all nodes |
kubectl get pv |
List all persistent volumes |
- Describe Resources:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl describe pod <pod_name> |
Describe a pod |
kubectl describe svc <service_name> |
Describe a service |
kubectl describe deploy <deployment_name> |
Describe a deployment |
kubectl describe node <node_name> |
Describe a node |
- Create, Edit, and Delete Resources:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl create -f <filename> |
Create a resource from a file |
kubectl apply -f <filename> |
Apply a configuration to a resource |
kubectl edit pod <pod_name> |
Edit a pod |
kubectl delete pod <pod_name> |
Delete a pod |
kubectl delete svc <service_name> |
Delete a service |
kubectl delete deploy <deployment_name> |
Delete a deployment |
- Execute Commands in Pods:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl exec -it <pod_name> -- <command> |
Execute a command in a pod |
kubectl logs <pod_name> |
Print the logs of a pod |
kubectl port-forward <pod_name> <local_port>:<pod_port> |
Forward ports to a pod |
- Scaling and Rolling Updates:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl scale deployment <deployment_name> --replicas=<replica_count> |
Scale a deployment |
kubectl rollout status deployment <deployment_name> |
Check the rollout status of a deployment |
kubectl rollout history deployment <deployment_name> |
View the rollout history of a deployment |
kubectl rollout undo deployment <deployment_name> |
Undo a deployment |
- Namespace Operations:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl get ns |
List all namespaces |
kubectl create ns <namespace_name> |
Create a namespace |
kubectl delete ns <namespace_name> |
Delete a namespace |
Step 9: Uninstalling Kubectl from Ubuntu
Kubectl binaries are saved in either of the following directories:
/snap/bin/kubectl
/usr/bin/kubectl
/usr/local/bin/kubectl
To uninstall Kubectl on Ubuntu, you’ll need to remove it based on the package manager you used.
Snap will save Kubectl on /snap/bin/kubectl. This way you will use the snap command to uninstall Kubectl as follows:
sudo snap remove kubectl
Binary saved on /usr/bin/kubectl or /usr/local/bin/kubectl uses apt. You should remove Kubectl on Ubuntu using apt as such:
sudo apt-get remove kubectl
Conclusion
This guide helped you. I hope you have Learned:
- How to install Kubectl on Ubuntu using Snap.
- Using apt package manager and Kubernetes apt repository to install Kubectl on Ubuntu server 20.04|22.04.
- install Ubuntu Kubectl binary using curl from the Kubernetes GitHub repository.
- Kubernetes Kubectl shorthand command you need to know and run on your Ubuntu server.
- Learn Ubuntu Kubectl commands cheat sheet.
- How to Install Kubernetes on Ubuntu.